Page 70 - Electrical Equipment Handbook _ Troubleshooting and Maintenance
P. 70
TRANSFORMERS
TRANSFORMERS 3.27
Apparent Power Rating of a Transformer
The apparent power rating of a transformer is used in conjunction with the voltage rating
to determine the maximum allowable current in the transformer. Since the heat losses are
2
proportional to i R, the current must be limited to prevent a significant reduction in the life
of the insulation due to overheating.
If the transformer is operated at a lower frequency than normal (say, 50 Hz rather than
60 Hz) and its applied voltage is reduced as discussed above, its apparent power rating must
be reduced by an equal amount. This is done to prevent overheating.
Inrush Current
The inrush current to the transformer is around 12 times the normal operating current. It
usually lasts 8 to 10 cycles. The transformer and the power system connected to it must be
able to withstand these high currents.
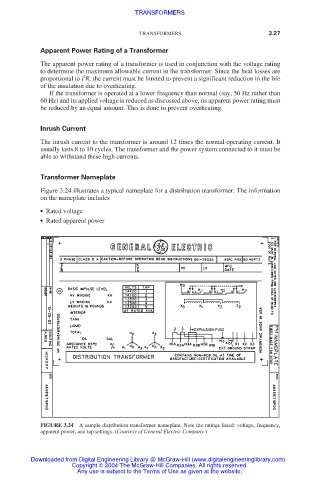
Transformer Nameplate
Figure 3.24 illustrates a typical nameplate for a distribution transformer. The information
on the nameplate includes
● Rated voltage
● Rated apparent power
FIGURE 3.24 A sample distribution transformer nameplate. Note the ratings listed: voltage, frequency,
apparent power, and tap settings. (Courtesy of General Electric Company.)
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.