Page 182 - Electrical Properties of Materials
P. 182
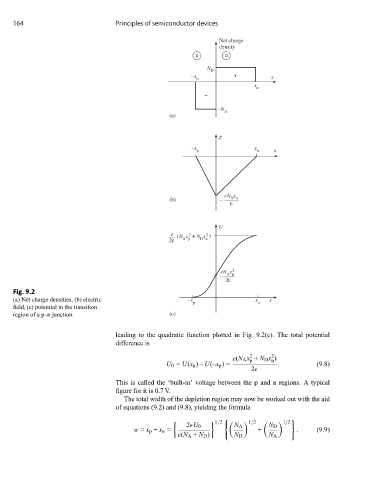
164 Principles of semiconductor devices
Net charge
density
p n
N
D
–x + x
p
x
n
–
–N A
(a)
–x p x n x
eN x
(b) D n
ε
U
e (N x + N x )
2
2
2ε A p D n
eN x 2
A p
2ε
Fig. 9.2
(a) Net charge densities, (b) electric –x x x
p n
field, (c) potential in the transition
region of a p–n junction. (c)
leading to the quadratic function plotted in Fig. 9.2(c). The total potential
difference is
2
2
e(N A x + N D x )
n
p
U 0 = U(x n )– U(–x p )= . (9.8)
2
This is called the ‘built-in’ voltage between the p and n regions. A typical
figure for it is 0.7 V.
The total width of the depletion region may now be worked out with the aid
of equations (9.2) and (9.8), yielding the formula
1/2 1/2 1/2
2 U 0 N A N D
w = x p + x n = + . (9.9)
e(N A + N D ) N D N A