Page 145 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 145
Chapter 6 Rotating Components 107
M M
Schematic Symbol
Schematic Symbol
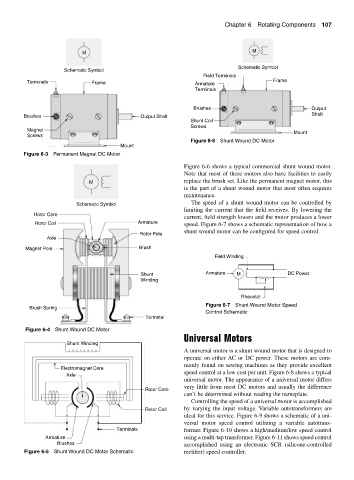
Field Terminals
Terminals Frame Armature Frame
Terminals
Brushes Output
Shaft
Brushes Output Shaft
Shunt Coil
Screws
Magnet
Mount
Screws
Figure 6-6 Shunt Wound DC Motor
Mount
Figure 6-3 Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Figure 6-6 shows a typical commercial shunt wound motor.
Note that most of these motors also have facilities to easily
M replace the brush set. Like the permanent magnet motor, this
is the part of a shunt wound motor that most often requires
maintenance.
The speed of a shunt wound motor can be controlled by
Schematic Symbol
limiting the current that the field receives. By lowering the
Rotor Core
current, field strength lowers and the motor produces a lower
Rotor Coil Armature speed. Figure 6-7 shows a schematic representation of how a
shunt wound motor can be configured for speed control.
Rotor Pole
Axle
Magnet Pole Brush
Field Winding
Shunt Armature M DC Power
Winding
Rheostat
Figure 6-7 Shunt Wound Motor Speed
Brush Spring
Control Schematic
Terminal
Figure 6-4 Shunt Wound DC Motor
Universal Motors
Shunt Winding
A universal motor is a shunt wound motor that is designed to
operate on either AC or DC power. These motors are com-
monly found on sewing machines as they provide excellent
Electromagnet Core
speed control at a low cost per unit. Figure 6-8 shows a typical
Axle
universal motor. The appearance of a universal motor differs
very little from most DC motors and usually the difference
Rotor Core
can’t be determined without reading the nameplate.
Controlling the speed of a universal motor is accomplished
Rotor Coil by varying the input voltage. Variable autotransformers are
ideal for this service. Figure 6-9 shows a schematic of a uni-
versal motor speed control utilizing a variable autotrans-
Terminals former. Figure 6-10 shows a high/medium/low speed control
Armature using a multi-tap transformer. Figure 6-11 shows speed control
Brushes accomplished using an electronic SCR (silicone-controlled
Figure 6-5 Shunt Wound DC Motor Schematic rectifier) speed controller.