Page 52 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 52
14 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
Solinoid 31.36" of Motion
Applied (MA)
12" of Vertical 25 Pounds of Force
Motion Generated Applied (FA) 100 Pounds
(VMG)
of Load (W)
22.5° (A)
Cable
28.97" of Horizontal Motion
Generated (HMG)
Pullys
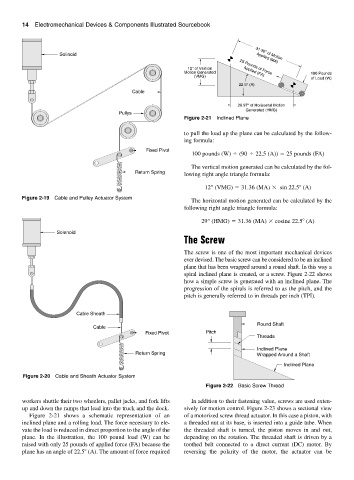
Figure 2-21 Inclined Plane
to pull the load up the plane can be calculated by the follow-
ing formula:
Fixed Pivot
100 pounds (W) (90 22.5 (A)) 25 pounds (FA)
The vertical motion generated can be calculated by the fol-
Return Spring lowing right angle triangle formula:
12" (VMG) 31.36 (MA) sin 22.5 (A)
Figure 2-19 Cable and Pulley Actuator System
The horizontal motion generated can be calculated by the
following right angle triangle formula:
29" (HMG) 31.36 (MA) cosine 22.5 (A)
Solenoid
The Screw
The screw is one of the most important mechanical devices
ever devised. The basic screw can be considered to be an inclined
plane that has been wrapped around a round shaft. In this way a
spiral inclined plane is created, or a screw. Figure 2-22 shows
how a simple screw is generated with an inclined plane. The
progression of the spirals is referred to as the pitch, and the
pitch is generally referred to in threads per inch (TPI).
Cable Sheath
Round Shaft
Cable
Fixed Pivot Pitch
Threads
Inclined Plane
Return Spring Wrapped Around a Shaft
Inclined Plane
Figure 2-20 Cable and Sheath Actuator System
Figure 2-22 Basic Screw Thread
workers shuttle their two wheelers, pallet jacks, and fork lifts In addition to their fastening value, screws are used exten-
up and down the ramps that lead into the truck and the dock. sively for motion control. Figure 2-23 shows a sectional view
Figure 2-21 shows a schematic representation of an of a motorized screw thread actuator. In this case a piston, with
inclined plane and a rolling load. The force necessary to ele- a threaded nut at its base, is inserted into a guide tube. When
vate the load is reduced in direct proportion to the angle of the the threaded shaft is turned, the piston moves in and out,
plane. In the illustration, the 100 pound load (W) can be depending on the rotation. The threaded shaft is driven by a
raised with only 25 pounds of applied force (FA) because the toothed belt connected to a direct current (DC) motor. By
plane has an angle of 22.5 (A). The amount of force required reversing the polarity of the motor, the actuator can be