Page 59 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 59
Chapter 3 Power Sources 21
−
+ It should be noted that the higher the surface area of the
plates, the greater the battery’s current capacity will be.
Negative Positive terminal Surface area can be gained by using either larger plates or a
Terminal higher plate count. The proximity of the plates to one another
will also affect current capacity. The closer the plates are to
one another, the higher the battery’s current capacity will be.
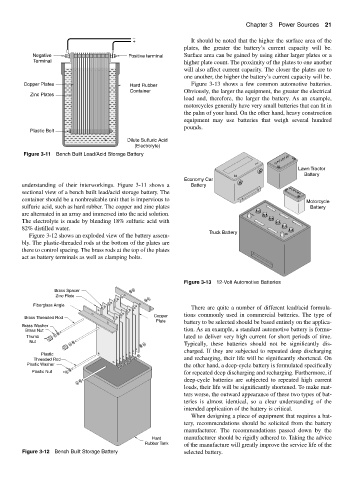
Copper Plates Hard Rubber Figure 3-13 shows a few common automotive batteries.
Container Obviously, the larger the equipment, the greater the electrical
Zinc Plates
load and, therefore, the larger the battery. As an example,
motorcycles generally have very small batteries that can fit in
the palm of your hand. On the other hand, heavy construction
equipment may use batteries that weigh several hundred
pounds.
Plastic Bolt
Dilute Sulfuric Acid
(Electrolyte)
Figure 3-11 Bench Built Lead/Acid Storage Battery
Lawn Tractor
Battery
Economy Car
understanding of their interworkings. Figure 3-11 shows a Battery
sectional view of a bench built lead/acid storage battery. The
container should be a nonbreakable unit that is impervious to Motorcycle
sulfuric acid, such as hard rubber. The copper and zinc plates Battery
are alternated in an array and immersed into the acid solution.
The electrolyte is made by blending 18% sulfuric acid with
82% distilled water.
Truck Battery
Figure 3-12 shows an exploded view of the battery assem-
bly. The plastic-threaded rods at the bottom of the plates are
there to control spacing. The brass rods at the top of the plates
act as battery terminals as well as clamping bolts.
Figure 3-13 12-Volt Automotive Batteries
Brass Spacer
Zinc Plate
Fiberglass Angle
There are quite a number of different lead/acid formula-
Copper tions commonly used in commercial batteries. The type of
Brass Threaded Rod
Plate battery to be selected should be based entirely on the applica-
Brass Washer
Brass Nut tion. As an example, a standard automotive battery is formu-
Thumb lated to deliver very high current for short periods of time.
Nut
Typically, these batteries should not be significantly dis-
charged. If they are subjected to repeated deep discharging
Plastic
Threaded Rod and recharging, their life will be significantly shortened. On
Plastic Washer the other hand, a deep-cycle battery is formulated specifically
Plastic Nut for repeated deep discharging and recharging. Furthermore, if
deep-cycle batteries are subjected to repeated high current
loads, their life will be significantly shortened. To make mat-
ters worse, the outward appearance of these two types of bat-
teries is almost identical, so a clear understanding of the
intended application of the battery is critical.
When designing a piece of equipment that requires a bat-
tery, recommendations should be solicited from the battery
manufacturer. The recommendations passed down by the
Hard manufacturer should be rigidly adhered to. Taking the advice
Rubber Tank of the manufacture will greatly improve the service life of the
Figure 3-12 Bench Built Storage Battery selected battery.