Page 64 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 64
26 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
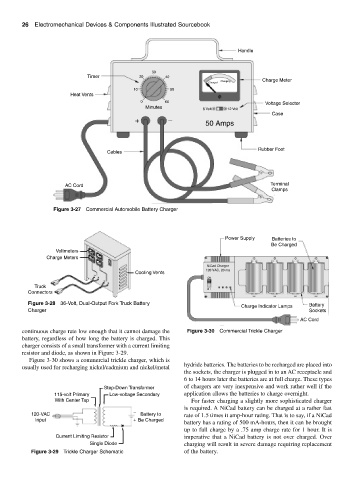
Handle
30
Timer 20 40
Charge Meter
Charging
Charged
10 50
Heat Vents
0 60 Voltage Selector
Minutes 6 Volt 12 Volt
Case
+ −
50 Amps
Rubber Foot
Cables
AC Cord Terminal
Clamps
Figure 3-27 Commercial Automobile Battery Charger
Power Supply Batteries to
Be Charged
Voltmeters
Charge Meters
NiCad Charger + + + +
120 VAC, 20 ma
Cooling Vents
ON
Truck
OFF
Connectors
Figure 3-28 36-Volt, Dual-Output Fork Truck Battery Battery
Charge Indicator Lamps
Charger Sockets
AC Cord
continuous charge rate low enough that it cannot damage the Figure 3-30 Commercial Trickle Charger
battery, regardless of how long the battery is charged. This
charger consists of a small transformer with a current limiting
resistor and diode, as shown in Figure 3-29.
Figure 3-30 shows a commercial trickle charger, which is
hydride batteries. The batteries to be recharged are placed into
usually used for recharging nickel/cadmium and nickel/metal
the sockets, the charger is plugged in to an AC receptacle and
6 to 14 hours later the batteries are at full charge. These types
Step-Down Transformer of chargers are very inexpensive and work rather well if the
115-volt Primary Low-voltage Secondary application allows the batteries to charge overnight.
With Center Tap For faster charging a slightly more sophisticated charger
is required. A NiCad battery can be charged at a rather fast
−
120-VAC Battery to rate of 1.5 times it amp-hour rating. That is to say, if a NiCad
Input + Be Charged
battery has a rating of 500 mA-hours, then it can be brought
up to full charge by a .75 amp charge rate for 1 hour. It is
Current Limiting Resistor imperative that a NiCad battery is not over charged. Over
Single Diode charging will result in severe damage requiring replacement
Figure 3-29 Trickle Charger Schematic of the battery.