Page 60 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 60
22 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
Dry Cells There are a variety of dry cell formulations that are com-
monly in the market. These include carbon/zinc, alkaline, sil-
Dry cells are the batteries that we are most familiar with. Dry ver oxide, mercury, lithium, nickel/cadmium, and nickel/metal
cells power most of our personal appliances like flashlights, cal- hydride. All of these different formulations have different
culators, cameras, and cell phones. The term “dry cell” can be a applications. As with the lead/acid batteries, recommendations
little deceiving. The electrolyte of these batteries are not really should be solicited from the battery manufacturer before
dry, rather it is a paste. Figure 3-14 shows an ordinary 1.5-volt designing a battery into a piece of equipment. The recommen-
dry cell battery. The positive terminal is a carbon rod. The neg- dations passed down by the manufacturer should be rigidly
ative terminal is a zinc container. The container has a liner made adhered to. The advice of the manufacturer is generally
of blotting paper. The electrolyte is a paste of sal-ammoniac and intended to improve the service life of the selected battery.
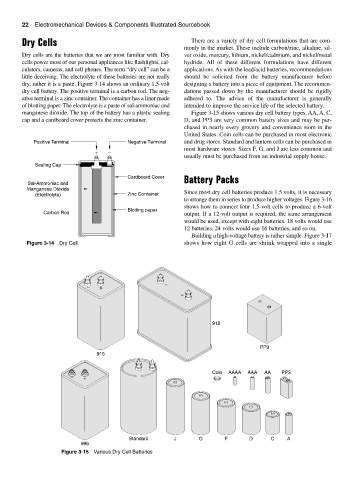
manganese dioxide. The top of the battery has a plastic sealing Figure 3-15 shows various dry cell battery types. AA, A, C,
cap and a cardboard cover protects the zinc container. D, and PP3 are very common battery sizes and may be pur-
chased in nearly every grocery and convenience store in the
United States. Coin cells can be purchased in most electronic
Positive Terminal Negative Terminal and drug stores. Standard and lantern cells can be purchased in
most hardware stores. Sizes F, G, and J are less common and
+ −
usually must be purchased from an industrial supply house.
Sealing Cap
Cardboard Cover Battery Packs
Sal-Ammoniac and
Manganese Dioxide
(Electrolyte) Zinc Container Since most dry cell batteries produce 1.5 volts, it is necessary
to arrange them in series to produce higher voltages. Figure 3-16
shows how to connect four 1.5-volt cells to produce a 6-volt
Blotting paper
Carbon Rod output. If a 12-volt output is required, the same arrangement
would be used, except with eight batteries. 18 volts would use
12 batteries, 24 volts would use 16 batteries, and so on.
Building a high-voltage battery is rather simple. Figure 3-17
Figure 3-14 Dry Cell shows how eight G cells are shrink wrapped into a single
− + −
+
918
PP9
915
Coin AAAA AAA AA PP3
− +
Standard J G F D C A
996
Figure 3-15 Various Dry Cell Batteries