Page 223 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 223
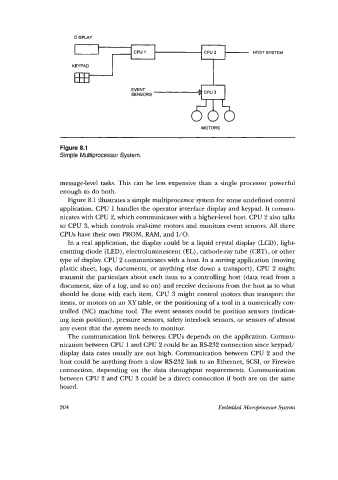
DISPLAY
HOST SYSTEM
KEYPAD
EVENT
SENSORS
MOTORS
Figure 8.1
Simple Multiprocessor System.
message-level tasks. This can be less expensive than a single processor powerful
enough to do both.
Figure 8.1 illustrates a simple multiprocessor system for some undefined control
application. CPU 1 handles the operator interface display and keypad. It commu-
nicates with CPU 2, which communicates with a higher-level host. CPU 2 also talks
to CPU 3, which controls real-time motors and monitors event sensors. All three
CPUs have their own PROM, RAM, and I/O.
In a real application, the display could be a liquid crystal display (LCD), light-
emitting diode (LED), electroluminescent (EL), cathode-ray tube (CRT), or other
type of display. CPU 2 communicates with a host. In a sorting application (moving
plastic sheet, logs, documents, or anything else down a transport), CPU 2 might
transmit the particulars about each item to a controlling host (data read from a
document, size of a log, and so on) and receive decisions from the host as to what
should be done with each item. CPU 3 might control motors that transport the
items, or motors on an XY table, or the positioning of a tool in a numerically con-
trolled (NC) machine tool. The event sensors could be position sensors (indicat-
ing item position), pressure sensors, safety interlock sensors, or sensors of almost
any event that the system needs to monitor.
The communication link between CPUs depends on the application. Commu-
nication between CPU 1 and CPU 2 could be an RS-232 connection since keypad/
display data rates usually are not high. Communication between CPU 2 and the
host could be anything from a slow RS232 link to an Ethernet, SCSI, or Firewire
connection, depending on the data throughput requirements. Communication
between CPU 2 and CPU 3 could be a direct connection if both are on the same
board.
204 Embedded Microprocessor Systems