Page 238 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 238
RS-485
TRANSCEIVER
RS-485
TRANSCEIVER
P
COMMUNICATION BUS
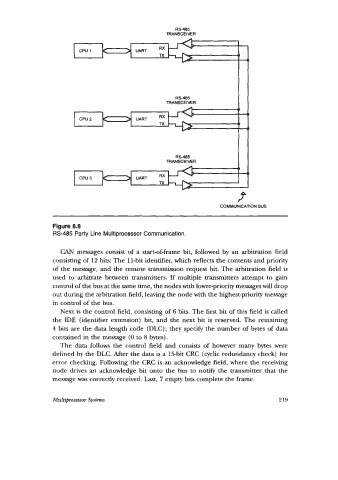
Figure 8.8
RS-485 Party Line Multiprocessor Communication.
CAN messages consist of a start-of-frame bit, followed by an arbitration field
consisting of 12 bits: The 1 1-bit identifier, which reflects the contents and priority
of the message, and the remote transmission request bit. The arbitration field is
used to arbitrate between transmitters. If multiple transmitters attempt to gain
control of the bus at the same time, the nodes with lower-priority messages will drop
out during the arbitration field, leaving the node with the highest-priority message
in control of the bus.
Next is the control field, consisting of 6 bits. The first bit of this field is called
the IDE (identifier extension) bit, and the next bit is reserved. The remaining
4 bits are the data length code (DLC); they spec@ the number of bytes of data
contained in the message (0 to 8 bytes).
The data follows the control field and consists of however many bytes were
defined by the DLC. After the data is a 15-bit CRC (cyclic redundancy check) for
error checking. Following the CRC is an acknowledge field, where the receiving
node drives an acknowledge bit onto the bus to now the transmitter that the
message was correctly received. Last, 7 empty bits complete the frame.
Multiprocessor Systems 219