Page 340 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 340
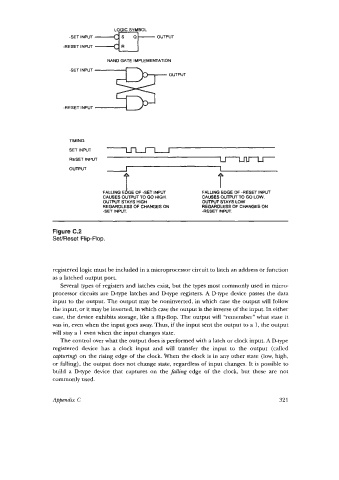
LOGIC SYMBOL
-SET INPUT *
OUTPUT
-RESET INPUT
NAND GATE IMPLEMENTATION
-SET INPUT
OUTPUl
-RESET INPUT
TIMING
SET INPUT
RESET INPUT U
OUTPUT I 1
f
FALLING E 1 OF -SET INPUT FALLING EDGE OF -RESET INPUT
GE
CAUSES OUTPUT TO GO HIGH. CAUSES OUTPUT TO GO LOW.
OUTPUT STAYS HIGH OUTPUT STAYS LOW
REGARDLESS OF CHANGES ON REGARDLESS OF CHANGES ON
-SET INPUT. -RESET INPUT.
Figure C.2
SeVReset Flip-Flop.
registered logic must be included in a microprocessor circuit to latch an address or function
as a latched output port.
Several types of registers and latches exist, but the types most commonly used in micro-
processor circuits are D-type latches and D-type registers. A D-type device passes the data
input to the output. The output may be noninverted, in which case the output will follow
the input, or it may be inverted, in which case the output is the inverse of the input. In either
case, the device exhibits storage, like a flip-flop. The output will “remember” what state it
was in, even when the input goes away. Thus, if the input sent the output to a 1, the output
will stay a 1 even when the input changes state.
The control over what the output does is performed with a latch or clock input. A D-type
registered device has a clock input and will transfer the input to the output (called
capturing) on the rising edge of the clock. When the clock is in any other state (low, high,
or falling), the output does not change state, regardless of input changes. It is possible to
build a D-type device that captures on the fulling edge of the clock, but these are not
commonly used.
Appendix C 321