Page 353 - Embedded Microprocessor Systems Real World Design
P. 353
MICROPROCESSOR IC
1 -
EXTERNAL CONTROL STORE
ADDR INDIRECT ADDRESS REGISTER
TYPICAL INSTRUCTION CYCLE:
EXTERNAL ADDRESS
EXTERNAL DATA
CONTROL STORE SELECT
MEMORY SELECT
/READ
INSTRUCTION REGISTER
CONTENTS
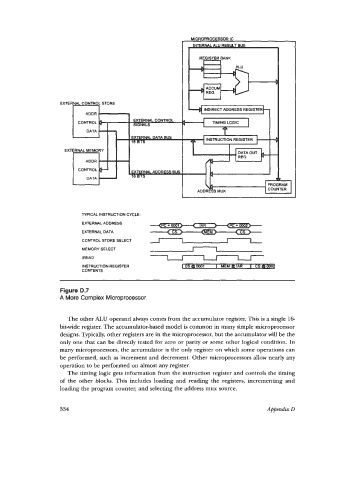
Figure D.7
A More Complex Microprocessor.
The other ALU operand always comes from the accumulator register. This is a single 16
bit-wide register. The accumulator-based model is common in many simple microprocessor
designs. Typically, other registers are in the microprocessor, but the accumulator will be the
only one that can be directly tested for zero or parity or some other logical condition. In
many microprocessors, the accumulator is the only register on which some operations can
be performed, such as increment and decrement. Other microprocessors allow nearly any
operation to be performed on almost any register.
The timing logic gets information from the instruction register and controls the timing
of the other blocks. This includes loading and reading the registers, incrementing and
loading the program counter, and selecting the address mux source.
334 Aj@ndix D