Page 138 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 138
P1: LEF/GUR Final Pages P2: GTV
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN007O-865 July 6, 2001 17:0
Image-Guided Surgery 587
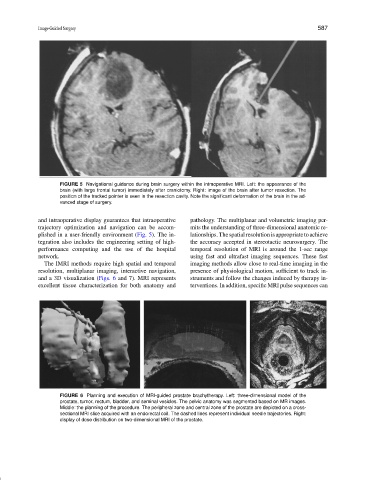
FIGURE 5 Navigational guidance during brain surgery within the intraoperative MRI. Left: the appearance of the
brain (with large frontal tumor) immediately after craniotomy. Right: image of the brain after tumor resection. The
position of the tracked pointer is seen in the resection cavity. Note the significant deformation of the brain in the ad-
vanced stage of surgery.
and intraoperative display guarantees that intraoperative pathology. The multiplanar and volumetric imaging per-
trajectory optimization and navigation can be accom- mits the understanding of three-dimensional anatomic re-
plished in a user-friendly environment (Fig. 5). The in- lationships.Thespatialresolutionisappropriatetoachieve
tegration also includes the engineering setting of high- the accuracy accepted in stereotactic neurosurgery. The
performance computing and the use of the hospital temporal resolution of MRI is around the 1-sec range
network. using fast and ultrafast imaging sequences. These fast
The IMRI methods require high spatial and temporal imaging methods allow close to real-time imaging in the
resolution, multiplanar imaging, interactive navigation, presence of physiological motion, sufficient to track in-
and a 3D visualization (Figs. 6 and 7). MRI represents struments and follow the changes induced by therapy in-
excellent tissue characterization for both anatomy and terventions. In addition, specific MRI pulse sequences can
FIGURE 6 Planning and execution of MRI-guided prostate brachytherapy. Left: three-dimensional model of the
prostate, tumor, rectum, bladder, and seminal vesicles. The pelvic anatomy was segmented based on MR images.
Middle: the planning of the procedure. The peripheral zone and central zone of the prostate are depicted on a cross-
sectional MRI slice acquired with an endorectal coil. The dashed lines represent individual needle trajectories. Right:
display of dose distribution on two-dimensional MRI of the prostate.