Page 68 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 68
P1: GRB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-67 May 25, 2001 20:8
250 Bioreactors
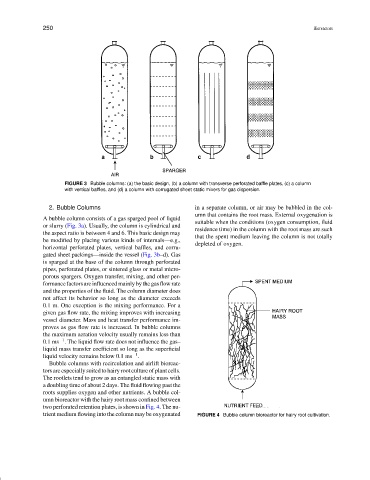
FIGURE 3 Bubble columns: (a) the basic design, (b) a column with transverse perforated baffle plates, (c) a column
with vertical baffles, and (d) a column with corrugated sheet static mixers for gas dispersion.
2. Bubble Columns in a separate column, or air may be bubbled in the col-
umn that contains the root mass. External oxygenation is
A bubble column consists of a gas sparged pool of liquid
suitable when the conditions (oxygen consumption, fluid
or slurry (Fig. 3a). Usually, the column is cylindrical and
residence time) in the column with the root mass are such
the aspect ratio is between 4 and 6. This basic design may
that the spent medium leaving the column is not totally
be modified by placing various kinds of internals—e.g.,
depleted of oxygen.
horizontal perforated plates, vertical baffles, and corru-
gated sheet packings—inside the vessel (Fig. 3b–d). Gas
is sparged at the base of the column through perforated
pipes, perforated plates, or sintered glass or metal micro-
porous spargers. Oxygen transfer, mixing, and other per-
formancefactors areinfluencedmainlybythegasflow rate
and the properties of the fluid. The column diameter does
not affect its behavior so long as the diameter exceeds
0.1 m. One exception is the mixing performance. For a
given gas flow rate, the mixing improves with increasing
vessel diameter. Mass and heat transfer performance im-
provesasgas flow rate is increased. In bubble columns
the maximum aeration velocity usually remains less than
−1
0.1 ms . The liquid flow rate does not influence the gas–
liquid mass transfer coefficient so long as the superficial
−1
liquid velocity remains below 0.1 ms .
Bubble columns with recirculation and airlift bioreac-
tors are especially suited to hairy root culture of plant cells.
The rootlets tend to grow as an entangled static mass with
a doubling time of about 2 days. The fluid flowing past the
roots supplies oxygen and other nutrients. A bubble col-
umn bioreactor with the hairy root mass confined between
two perforated retention plates, is shown in Fig. 4. The nu-
trient medium flowing into the column may be oxygenated FIGURE 4 Bubble column bioreactor for hairy root cultivation.