Page 160 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 160
P1: GPAFinal Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-616 July 27, 2001 12:5
200 Protein Structure
(a) (b) (c)
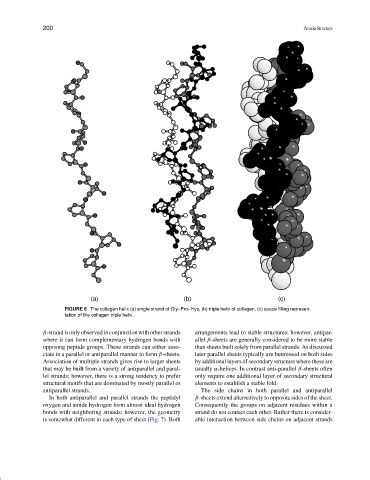
FIGURE 6 The collagen helix (a) single strand of Gly–Pro–Hyp, (b) triple helix of collagen, (c) space filling represen-
tation of the collagen triple helix.
β-strandisonlyobservedinconjunctionwithotherstrands arrangements lead to stable structures; however, antipar-
where it can form complementary hydrogen bonds with allel β-sheets are generally considered to be more stable
opposing peptide groups. These strands can either asso- than sheets built solely from parallel strands. As discussed
ciate in a parallel or antiparallel manner to form β-sheets. later parallel sheets typically are buttressed on both sides
Association of multiple strands gives rise to larger sheets by additional layers of secondary structure where these are
that may be built from a variety of antiparallel and paral- usually α-helices. In contrast anti-parallel β-sheets often
lel strands; however, there is a strong tendency to prefer only require one additional layer of secondary structural
structural motifs that are dominated by mostly parallel or elements to establish a stable fold.
antiparallel strands. The side chains in both parallel and antiparallel
In both antiparallel and parallel strands the peptidyl β-sheets extend alternatively to opposite sides of the sheet.
oxygen and amide hydrogen form almost ideal hydrogen Consequently the groups on adjacent residues within a
bonds with neighboring strands; however, the geometry strand do not contact each other. Rather there is consider-
is somewhat different in each type of sheet (Fig. 7). Both able interaction between side chains on adjacent strands