Page 158 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 158
P1: GPAFinal Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-616 July 27, 2001 12:5
198 Protein Structure
Anti-parallel β-strand
Parallel β-strand
Left-handed
α-helix
ψ
Right-handed
α-helix
φ
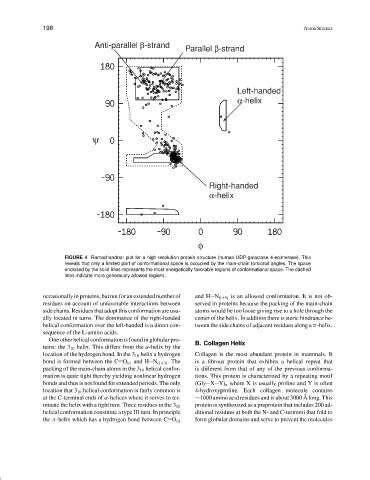
FIGURE 4 Ramachandran plot for a high-resolution protein structure (human UDP-galactose 4-epimerase). This
reveals that only a limited part of conformational space is occupied by the main-chain torsional angles. The space
enclosed by the solid lines represents the most energetically favorable regions of conformational space. The dashed
lines indicate more generously allowed regions.
occasionally in proteins, but not for an extended number of and H N (i+5) is an allowed conformation. It is not ob-
residues on account of unfavorable interactions between served in proteins because the packing of the main-chain
side chains. Residues that adopt this conformation are usu- atoms would be too loose giving rise to a hole through the
ally located in turns. The dominance of the right-handed center of the helix. In addition there is steric hindrance be-
helical conformation over the left-handed is a direct con- tween the side chains of adjacent residues along a π-helix.
sequence of the L-amino acids.
One other helical conformation is found in globular pro- B. Collagen Helix
teins: the 3 10 helix. This differs from the α-helix by the
location of the hydrogen bond. In the 3 10 helix a hydrogen Collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals. It
bond is formed between the C O (i) and H N (i+3) . The is a fibrous protein that exhibits a helical repeat that
packing of the main-chain atoms in the 3 10 helical confor- is different from that of any of the previous conforma-
mation is quite tight thereby yielding nonlinear hydrogen tions. This protein is characterized by a repeating motif
bonds and thus is not found for extended periods. The only (Gly X Y) n where X is usually proline and Y is often
location that 3 10 helical conformation is fairly common is 4-hydroxyproline. Each collagen molecule contains
˚
at the C-terminal ends of α-helices where it serves to ter- ∼1000 amino acid residues and is about 3000 A long. This
protein is synthesized as a preprotein that includes 200 ad-
minate the helix with a tight turn. Three residues in the 3 10
helical conformation constitute a type III turn. In principle ditional residues at both the N- and C-terminii that fold to
form globular domains and serve to prevent the molecules
the π-helix which has a hydrogen bond between C O (i)