Page 43 - Subyek Encyclopedia - Encyclopedia of Separation Science
P. 43
38 I / CENTRIFUGATION/ Derivatization
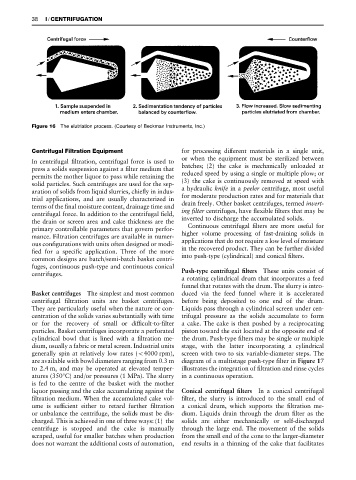
Figure 16 The elutriation process. (Courtesy of Beckman Instruments, Inc.)
Centrifugal Filtration Equipment for processing different materials in a single unit,
or when the equipment must be sterilized between
In centrifugal Rltration, centrifugal force is used to
press a solids suspension against a Rlter medium that batches; (2) the cake is mechanically unloaded at
permits the mother liquor to pass while retaining the reduced speed by using a single or multiple plow; or
(3) the cake is continuously removed at speed with
solid particles. Such centrifuges are used for the sep-
a hydraulic knife in a peeler centrifuge, most useful
aration of solids from liquid slurries, chieSy in indus-
for moderate production rates and for materials that
trial applications, and are usually characterized in
drain freely. Other basket centrifuges, termed invert-
terms of the Rnal moisture content, drainage time and
ing Tlter centrifuges, have Sexible Rlters that may be
centrifugal force. In addition to the centrifugal Reld,
inverted to discharge the accumulated solids.
the drain or screen area and cake thickness are the
primary controllable parameters that govern perfor- Continuous centrifugal Rlters are more useful for
mance. Filtration centrifuges are available in numer- higher volume processing of fast-draining solids in
ous conRgurations with units often designed or modi- applications that do not require a low level of moisture
Red for a speciRc application. Three of the more in the recovered product. They can be further divided
common designs are batch/semi-batch basket centri- into push-type (cylindrical) and conical Rlters.
fuges, continuous push-type and continuous conical
centrifuges. Push-type centrifugal Vlters These units consist of
a rotating cylindrical drum that incorporates a feed
funnel that rotates with the drum. The slurry is intro-
Basket centrifuges The simplest and most common duced via the feed funnel where it is accelerated
centrifugal Rltration units are basket centrifuges. before being deposited to one end of the drum.
They are particularly useful when the nature or con- Liquids pass through a cylindrical screen under cen-
centration of the solids varies substantially with time trifugal pressure as the solids accumulate to form
or for the recovery of small or difRcult-to-Rlter a cake. The cake is then pushed by a reciprocating
particles. Basket centrifuges incorporate a perforated piston toward the exit located at the opposite end of
cylindrical bowl that is lined with a Rltration me- the drum. Push-type Rlters may be single or multiple
dium, usually a fabric or metal screen. Industrial units stage, with the latter incorporating a cylindrical
generally spin at relatively low rates ((4000 rpm), screen with two to six variable-diameter steps. The
are available with bowl diameters ranging from 0.3 m diagram of a multistage push-type Rlter in Figure 17
to 2.4 m, and may be operated at elevated temper- illustrates the integration of Rltration and rinse cycles
atures (3503C) and/or pressures (1 MPa). The slurry in a continuous operation.
is fed to the centre of the basket with the mother
liquor passing and the cake accumulating against the Conical centrifugal Vlters In a conical centrifugal
Rltration medium. When the accumulated cake vol- Rlter, the slurry is introduced to the small end of
ume is sufRcient either to retard further Rltration a conical drum, which supports the Rltration me-
or unbalance the centrifuge, the solids must be dis- dium. Liquids drain through the drum Rlter as the
charged. This is achieved in one of three ways: (1) the solids are either mechanically or self-discharged
centrifuge is stopped and the cake is manually through the large end. The movement of the solids
scraped, useful for smaller batches when production from the small end of the cone to the larger-diameter
does not warrant the additional costs of automation, end results in a thinning of the cake that facilitates