Page 47 - Subyek Encyclopedia - Encyclopedia of Separation Science
P. 47
42 I / CHROMATOGRAPHY/ Derivatization
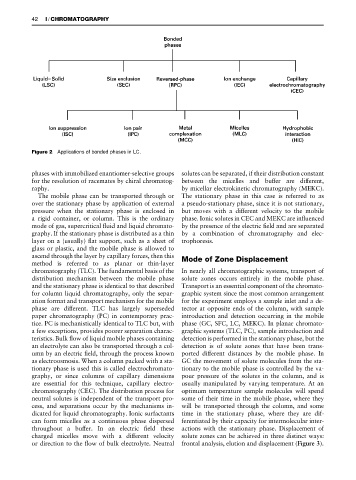
Figure 2 Applications of bonded phases in LC.
phases with immobilized enantiomer-selective groups solutes can be separated, if their distribution constant
for the resolution of racemates by chiral chromatog- between the micelles and buffer are different,
raphy. by micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC).
The mobile phase can be transported through or The stationary phase in this case is referred to as
over the stationary phase by application of external a pseudo-stationary phase, since it is not stationary,
pressure when the stationary phase is enclosed in but moves with a different velocity to the mobile
a rigid container, or column. This is the ordinary phase. Ionic solutes in CEC and MEKC are inSuenced
mode of gas, supercritical Suid and liquid chromato- by the presence of the electric Reld and are separated
graphy. If the stationary phase is distributed as a thin by a combination of chromatography and elec-
layer on a (usually) Sat support, such as a sheet of trophoresis.
glass or plastic, and the mobile phase is allowed to
ascend through the layer by capillary forces, then this Mode of Zone Displacement
method is referred to as planar or thin-layer
chromatography (TLC). The fundamental basis of the In nearly all chromatographic systems, transport of
distribution mechanism between the mobile phase solute zones occurs entirely in the mobile phase.
and the stationary phase is identical to that described Transport is an essential component of the chromato-
for column liquid chromatography, only the separ- graphic system since the most common arrangement
ation format and transport mechanism for the mobile for the experiment employs a sample inlet and a de-
phase are different. TLC has largely superseded tector at opposite ends of the column, with sample
paper chromatography (PC) in contemporary prac- introduction and detection occurring in the mobile
tice. PC is mechanistically identical to TLC but, with phase (GC, SFC, LC, MEKC). In planar chromato-
a few exceptions, provides poorer separation charac- graphic systems (TLC, PC), sample introduction and
teristics. Bulk Sow of liquid mobile phases containing detection is performed in the stationary phase, but the
an electrolyte can also be transported through a col- detection is of solute zones that have been trans-
umn by an electric Reld, through the process known ported different distances by the mobile phase. In
as electroosmosis. When a column packed with a sta- GC the movement of solute molecules from the sta-
tionary phase is used this is called electrochromato- tionary to the mobile phase is controlled by the va-
graphy, or since columns of capillary dimensions pour pressure of the solutes in the column, and is
are essential for this technique, capillary electro- usually manipulated by varying temperature. At an
chromatography (CEC). The distribution process for optimum temperature sample molecules will spend
neutral solutes is independent of the transport pro- some of their time in the mobile phase, where they
cess, and separations occur by the mechanisms in- will be transported through the column, and some
dicated for liquid chromatography. Ionic surfactants time in the stationary phase, where they are dif-
can form micelles as a continuous phase dispersed ferentiated by their capacity for intermolecular inter-
throughout a buffer. In an electric Reld these actions with the stationary phase. Displacement of
charged micelles move with a different velocity solute zones can be achieved in three distinct ways:
or direction to the Sow of bulk electrolyte. Neutral frontal analysis, elution and displacement (Figure 3).