Page 39 - Subyek Encyclopedia - Encyclopedia of Separation Science
P. 39
34 I / CENTRIFUGATION/ Derivatization
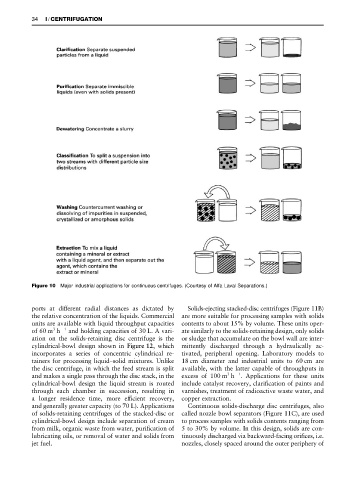
Figure 10 Major industrial applications for continuous centrifuges. (Courtesy of Alfa Laval Separations.)
ports at different radial distances as dictated by Solids-ejecting stacked-disc centrifuges (Figure 11B)
the relative concentration of the liquids. Commercial are more suitable for processing samples with solids
units are available with liquid throughput capacities contents to about 15% by volume. These units oper-
3
1
of 60 m h and holding capacities of 30 L. A vari- ate similarly to the solids-retaining design, only solids
ation on the solids-retaining disc centrifuge is the or sludge that accumulate on the bowl wall are inter-
cylindrical-bowl design shown in Figure 12, which mittently discharged through a hydraulically ac-
incorporates a series of concentric cylindrical re- tivated, peripheral opening. Laboratory models to
tainers for processing liquid}solid mixtures. Unlike 18 cm diameter and industrial units to 60 cm are
the disc centrifuge, in which the feed stream is split available, with the latter capable of throughputs in
3
1
and makes a single pass through the disc stack, in the excess of 100 m h . Applications for these units
cylindrical-bowl design the liquid stream is routed include catalyst recovery, clariRcation of paints and
through each chamber in succession, resulting in varnishes, treatment of radioactive waste water, and
a longer residence time, more efRcient recovery, copper extraction.
and generally greater capacity (to 70 L). Applications Continuous solids-discharge disc centrifuges, also
of solids-retaining centrifuges of the stacked-disc or called nozzle bowl separators (Figure 11C), are used
cylindrical-bowl design include separation of cream to process samples with solids contents ranging from
from milk, organic waste from water, puriRcation of 5 to 30% by volume. In this design, solids are con-
lubricating oils, or removal of water and solids from tinuously discharged via backward-facing oriRces, i.e.
jet fuel. nozzles, closely spaced around the outer periphery of