Page 171 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 171
Chapter 4. Micromechanics of stress transfer 153
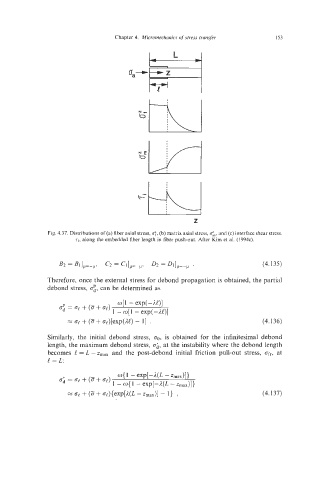
Fig. 4.37. Distributions of (a) fiber axial stress, cf,, (b) matrix axial stress, d,. and (c) interface shear stress.
~i. along the embedded fiber length In fiber push-out. After Kim et al. (1994~).
Therefore, once the external stress for debond propagation is obtained, the partial
debond stress, nz, can be determined as
= Q + (a + Oe)[exp(U) - 11 . (4.136)
Similarly, the initial debond stress, 00, is obtained for the infinitesimal debond
length, the maximum debond stress, o;, at the instability where the debond length
becomes e= L - zmax and the post-debond initial friction pull-out stress, Ofr, at
e = L:
O{ 1 - exp[-i(L - zmax)]}
0; = bp + (8 + Oe)
1 - O{ 1 - exp[-%(L - zmax)]}
(4.137)