Page 176 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 176
158 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
(a) (b)
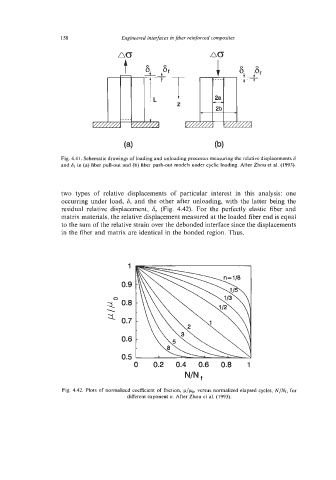
Fig. 4.41. Schematic drawings of loading and unloading processes measuring the relative displacements 6
and 6, in (a) fiber pull-out and (b) fiber push-out models under cyclic loading. After Zhou et al. (1993).
two types of relative displacements of particular interest in this analysis: one
occurring under load, 6, and the other after unloading, with the latter being the
residual relative displacement, 6, (Fig. 4.42). For the perfectly elastic fiber and
matrix materials, the relative displacement measured at the loaded fiber end is equal
to the sum of the relative strain over the debonded interface since the displacements
in the fiber and matrix are identical in the bonded region. Thus,
1
0.9
0
y 0.8
1
0.7
0.6
0.5
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
N/N f
Fig. 4.42. Plots of normalized coefficient of friction, p/b. versus normalized elapsed cycles, N/Nf, for
different exponent n. After Zhou et al. (1993).