Page 180 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 180
162 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
h
E 30
E
W
\ 25
5 20
c
Q)
n 15
C
0
II
Q) 10
n
5' 4 I I I I
-
0 2 4 6 81012
(4 Number of cycles, N
n
E 30
E
25
5 20
C
Q)
< 15
c
0
II
a, 10
n I 1 1'3
El I I I I I
-0 2 4 6 8 10 12
(b) Number of cycles, N
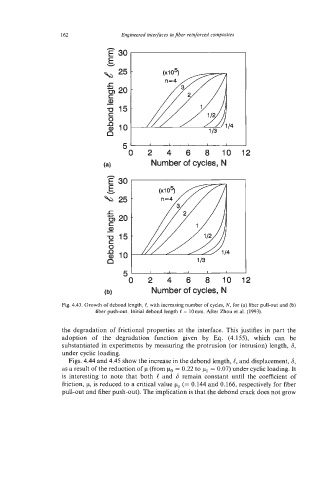
Fig. 4.43. Growth of debond length, e, with increasing number of cycles, N, for (a) fiber pull-out and (b)
fiber push-out. Initial debond length e= 10mm. After Zhou et al. (1993).
the degradation of frictional properties at the interface. This justifies in part the
adoption of the degradation function given by Eq. (4.155), which can be
substantiated in experiments by measuring the protrusion (or intrusion) length, 6,
under cyclic loading.
Figs. 4.44 and 4.45 show the increase in the debond length, C, and displacement, 6,
as a result of the reduction of p (from p,, = 0.22 to p1 = 0.07) under cyclic loading. It
is interesting to note that both C and 6 remain constant until the coefficient of
friction, p, is reduced to a critical value pc (= 0.144 and 0.166, respectively for fiber
pull-out and fiber push-out). The implication is that the debond crack does not grow