Page 181 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 181
Chapter 4. Micromechanics of stress transfer 163
1 I I
0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25
Coefficient of Friction,
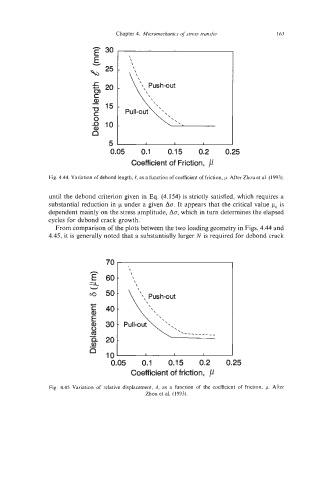
Fig. 4.44. Variation of debond length, e, as a function of coefficient of friction, p. After Zhou et al. (1993).
until the debond criterion given in Eq. (4.154) is strictly satisfied, which requires a
substantial reduction in p under a given ACT. It appears that the critical value pc is
dependent mainly on the stress amplitude, ACT, which in turn determines the elapsed
cycles for debond crack growth.
From comparison of the plots between the two loading geometry in Figs. 4.44 and
4.45, it is generally noted that a substantially larger N is required for debond crack
70
n
E 60
a
Y
a 50
40
Q)
5 30
0
cd
-E. 20
v)
b- 10
0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25
Coefficient of friction,
Fig. 4.45 Variation of relative displacement, 6, as a function of the coefficient of friction, p. After
Zhou et al. (1993).