Page 359 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 359
340 Engineered interfaces in Jiber reinforced composites
80
. AS44501-6
h
(u - IM7/gEEK It
6 60 AS4/tEEK f
v lM71377-2
Q T8004.3900-2
0 I
5 40 - AS4IULXEM1000 It
Q) 00 0 d
P
Impact energy (J)
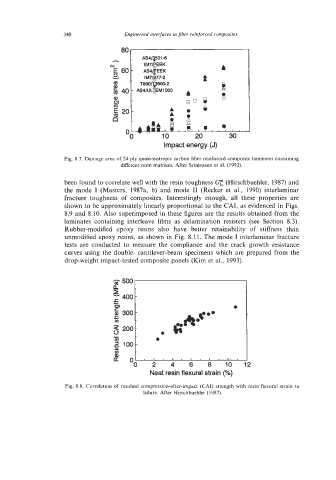
Fig. 8.7. Damage area of 24 ply quasi-isotropic carbon fiber reinforced composite laminates containing
different resin matrices. After Srinivasan et al. (1992).
been found to correlate well with the resin toughness (Hirschbuehler, 1987) and
the mode I (Masters, 1987a, b) and mode I1 (Recker et al., 1990) interlaminar
fracture toughness of composites. Interestingly enough, all these properties are
shown to be approximately linearly proportional to the CAI, as evidenced in Figs.
8.9 and 8.10. Also superimposed in these figures are the results obtained from the
laminates containing interleave films as delamination resisters (see Section 8.3).
Rubber-modified epoxy resins also have better retainability of stiffness than
unmodified epoxy resins, as shown in Fig. 8.11. The mode I interlaminar fracture
tests are conducted to measure the compliance and the crack growth resistance
curves using the double- cantilever-beam specimens which are prepared from the
drop-weight impact-tested composite panels (Kim et al., 1993).
e
(d e
+ 100-
.-
rn
E
2
Fig. 8.8. Correlation of residual compression-after-impact (CAI) strength with resin flexural strain to
failure. After Hirschbuehler (1987).