Page 749 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 749
14.10 DETECTION AND ELIMINATION OF TIMING DEFECTS 715
subscripts E and D refer to the E-hazard and d-trio, respectively. Following the procedure
given in Subsection 14.10.3, a brief inspection of these NS functions indicates that they are
free of static hazards.
^PathtoRG E
A
. o)
*y,y 0 Y o = y + M + ?,* (14 2
0
IP E
ORing RG E
-^v
Y 0 = y QA
Y,= y 0B + jjA + yjy 0
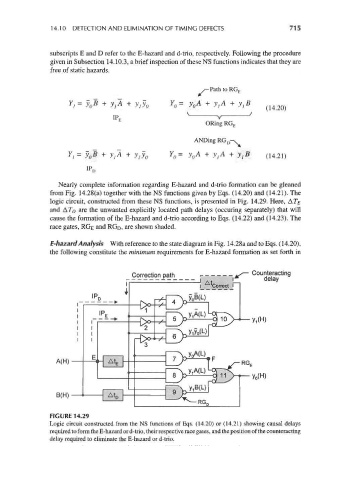
Nearly complete information regarding E-hazard and d-trio formation can be gleaned
from Fig. 14.28(a) together with the NS functions given by Eqs. (14.20) and (14.21). The
logic circuit, constructed from these NS functions, is presented in Fig. 14.29. Here, AT E
and A r D are the unwanted explicitly located path delays (occuring separately) that will
cause the formation of the E-hazard and d-trio according to Eqs. (14.22) and (14.23). The
race gates, RGe and RGo, are shown shaded.
E-hazard Analysis With reference to the state diagram in Fig. 14.28a and to Eqs. (14.20),
the following constitute the minimum requirements for E-hazard formation as set forth in
Correction path ^ ,^~ Cou S52, ctln 9
i A * ' aeiay
A(H)
B(H)
FIGURE 14.29
Logic circuit constructed from the NS functions of Eqs. (14.20) or (14.21) showing causal delays
required to form the E-hazard or d-trio, their respective race gates, and the position of the counteracting
delay required to eliminate the E-hazard or d-trio.