Page 336 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 336
294 Engineering Plastics
achieve the target molecular weight, these reagents should be charged as
part of the initial charge of reactants to the reactor system. The exact
amounts of end-capping agent or excess DCDPS monomer can be calcu-
lated on the basis of Carothers’stoichiometric functionality equations that
apply to an AA-BB type of condensation polymerization.
The polymerization of PES and PPSF proceeds in a similar manner to
that of PSF, but unlike the two-step process described for PSF, the bisphe-
nol S or the biphenol is now reacted directly with the DCDPS in the pres-
ence of a stoichiometric amount of base without the need for a separate
first step to convert the bisphenol to its dialkali salt derivative. Another
difference between the polymerizations of PES and PPSF as compared to
the PSF synthesis process is the need for a higher-boiling-point solvent to
handle the higher polymerization temperatures that are needed for these
polymers. Suitable solvents for the production of PES and PPSF include
NMP, dimethyl acetamide, diphenylsulfone, and sulfolane. A minor
cosolvent such as chlorobenzene or toluene can again be used to help keep
the reaction medium dehydrated. The most suitable base for use in PES
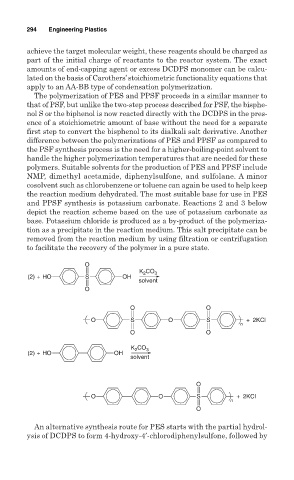
and PPSF synthesis is potassium carbonate. Reactions 2 and 3 below
depict the reaction scheme based on the use of potassium carbonate as
base. Potassium chloride is produced as a by-product of the polymeriza-
tion as a precipitate in the reaction medium. This salt precipitate can be
removed from the reaction medium by using filtration or centrifugation
to facilitate the recovery of the polymer in a pure state.
O
CO
K 2 3
(2) + HO S OH
solvent
O
O O
O S O S + 2KCl
n
O O
K CO 3
2
(2) + HO OH
solvent
O
O O S + 2KCl
n
O
An alternative synthesis route for PES starts with the partial hydrol-
ysis of DCDPS to form 4-hydroxy-4′-chlorodiphenylsulfone, followed by