Page 241 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 241
226
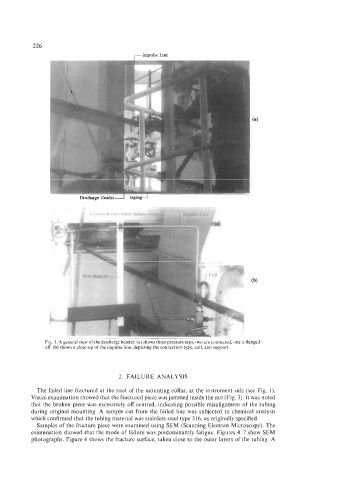
,- Impulsc Linc
Fig. 1. A general view of the discharge header: (a) shows three pressure taps, two are connected, one is flanged-
off. (b) shows a close-up of the impulse line, depicting the connection-type, coil, and support.
2. FAILURE ANALYSIS
The failed line fractured at the root of the mounting collar, at the instrument side (see Fig. 1).
Visual examination showed that the fractured piece was jammed inside the nut (Fig. 3). It was noted
that the broken piece was excessively off centred, indicating possible misalignment of the tubing
during original mounting. A sample cut from the failed line was subjected to chemical analysis
which confirmed that the tubing material was stainless steel type 3 16, as originally specified.
Samples of the fracture piece were examined using SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy). The
examination showed that the mode of failure was predominantly fatigue. Figures 4-7 show SEM
photographs. Figure 4 shows the fracture surface, taken close to the outer layers of the tubing. A