Page 134 - Finite Element Modeling and Simulations with ANSYS Workbench
P. 134
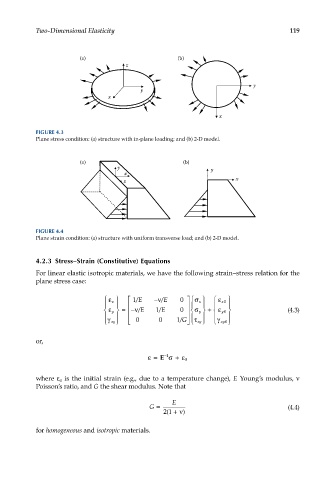
Two-Dimensional Elasticity 119
(a) (b)
z
y
y
x
x
FIGURE 4.3
Plane stress condition: (a) structure with in-plane loading; and (b) 2-D model.
(a) (b)
y y
x
z x
FIGURE 4.4
Plane strain condition: (a) structure with uniform transverse load; and (b) 2-D model.
4.2.3 Stress–Strain (Constitutive) Equations
For linear elastic isotropic materials, we have the following strain–stress relation for the
plane stress case:
ε 1/ E −ν E/ 0 σ x ε x0
x
/
ε = −ν E 1/ E 0 σ y + ε y0 (4.3)
y
0 0 1/ G
τ xy
γ xy γ xy0
or,
ε= E −1
σ+ ε 0
where ε is the initial strain (e.g., due to a temperature change), E Young’s modulus, ν
0
Poisson’s ratio, and G the shear modulus. Note that
E
G = (4.4)
21 ( + )ν
for homogeneous and isotropic materials.