Page 285 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 285
Flexible robotic platform with multiple-bending tendon-driven mechanism 275
Table 12.1: Calculation for the CPM of the stepper motors for the motor unit module.
Lead screw threads per cm 10 Number of threads in the lead screws
Number of starts 2
Turns per cm 2 10 threads per cm42 starts. Hence, it takes 5 revolutions to move 1 cm
CPM (cm per minute) 60 300 RPM45 revolutions per cm
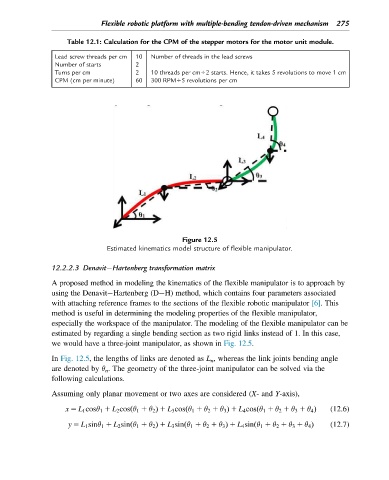
Figure 12.5
Estimated kinematics model structure of flexible manipulator.
12.2.2.3 Denavit Hartenberg transformation matrix
A proposed method in modeling the kinematics of the flexible manipulator is to approach by
using the Denavit Hartenberg (D H) method, which contains four parameters associated
with attaching reference frames to the sections of the flexible robotic manipulator [6].This
method is useful in determining the modeling properties of the flexible manipulator,
especially the workspace of the manipulator. The modeling of the flexible manipulator can be
estimated by regarding a single bending section as two rigid links instead of 1. In this case,
we would have a three-joint manipulator, as shown in Fig. 12.5.
In Fig. 12.5, the lengths of links are denoted as L n , whereas the link joints bending angle
are denoted by θ n . The geometry of the three-joint manipulator can be solved via the
following calculations.
Assuming only planar movement or two axes are considered (X- and Y-axis),
ð
ð
ð
x 5 L 1 cosθ 1 1 L 2 cos θ 1 1 θ 2 Þ 1 L 3 cos θ 1 1 θ 2 1 θ 3 Þ 1 L 4 cos θ 1 1 θ 2 1 θ 3 1 θ 4 Þ (12.6)
ð
y 5 L 1 sinθ 1 1 L 2 sin θ 1 1 θ 2 Þ 1 L 3 sin θ 1 1 θ 2 1 θ 3 Þ 1 L 4 sin θ 1 1 θ 2 1 θ 3 1 θ 4 Þ (12.7)
ð
ð