Page 527 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 527
Be st Practice 8 .12 Pump Mechanical Seal Flush Best Practices
B.P. 8.12. Supporting Material sure. In addition, as the process side seal leaks in this flush plan,
the atmospheric side seal will essentially be sealing the pumped
fluid, exposing the plant to the release of flammable and/or toxic
API Flush Plan 52
vapors.
Monitoring of seal leaks can be done by checking the level and
Dual un-pressurized seals (tandem) rely on a buffer fluid at or pressure of the reservoir, as one or both may increase in the
near atmospheric pressure to lubricate the atmospheric side event of excessive leakage. The seal vendor (or support system
seal. This buffer fluid is circulated via a pumping ring from the vendor) may supply high level and/or pressure switches which
seal to the seal reservoir and back to the seal (in a closed loop). would alert the operators to a seal leak. It is highly recom-
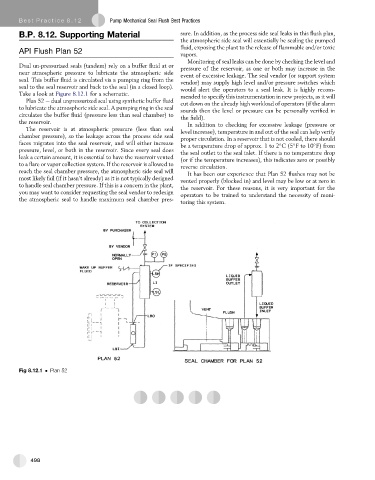
Take a look at Figure 8.12.1 for a schematic. mended to specify this instrumentation in new projects, as it will
Plan 52 e dual unpressurized seal using synthetic buffer fluid cut down on the already high workload of operators (if the alarm
to lubricate the atmospheric side seal. A pumping ring in the seal sounds then the level or pressure can be personally verified in
circulates the buffer fluid (pressure less than seal chamber) to
the field).
the reservoir. In addition to checking for excessive leakage (pressure or
The reservoir is at atmospheric pressure (less than seal
level increase), temperature in and out of the seal can help verify
chamber pressure), so the leakage across the process side seal proper circulation. In a reservoir that is not cooled, there should
faces migrates into the seal reservoir, and will either increase be a temperature drop of approx. 1 to 2 C(5 Fto10 F) from
pressure, level, or both in the reservoir. Since every seal does the seal outlet to the seal inlet. If there is no temperature drop
leak a certain amount, it is essential to have the reservoir vented (or if the temperature increases), this indicates zero or possibly
to a flare or vapor collection system. If the reservoir is allowed to reverse circulation.
reach the seal chamber pressure, the atmospheric side seal will It has been our experience that Plan 52 flushes may not be
most likely fail (if it hasn’t already) as it is not typically designed vented properly (blocked in) and level may be low or at zero in
to handle seal chamber pressure. If this is a concern in the plant, the reservoir. For these reasons, it is very important for the
you may want to consider requesting the seal vendor to redesign operators to be trained to understand the necessity of moni-
the atmospheric seal to handle maximum seal chamber pres-
toring this system.
Fig 8.12.1 Plan 52
498