Page 81 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 81
Pump Best Practices Best Practice 2 .10
Best
Best Practice 2.10Practice 2.10
Install discharge flange orifices for centrifugal pumps with produce a performance curve characteristic of sufficient
less than 5% head rise to ensure stable pump operation. head rise will lead to low pump MTBF.
Centrifugal pumps with flat head vs. flow curves (less than 5% head Low head rise curves, less than 5%, have resulted in the following
rise from rated to zero flow) produce rapid flow changes for small reliability issues:
process changes. Rapid inducer and/or impeller wear
Size the impeller for increased head (to compensate for the orifice Pump seizure
pressure drop). Bearing failure
Installing a discharge orifice in the pump volute or on the discharge Seal failure
flange will produce the desired head rise, and will result in a pump Shaft breakage
characteristic that produces gradual flow changes for small process Gear box failure
changes.
This procedure is especially effective for high speed pumps which
have a characteristic flat, low head rise performance curve. Benchmarks
This best practice has been used since the mid-1970s in all high speed
Lessons Learned pump applications, and where any centrifugal pump had a low head
Failure to correct pumps, especially high speed type rise characteristic. This has resulted in centrifugal pump operation of
(integral gear centrifugal), with discharge orifices, to optimum safety and reliability. MTBFs using this best practice have
been greater than 80 months.
B.P. 2.10. Supporting Material
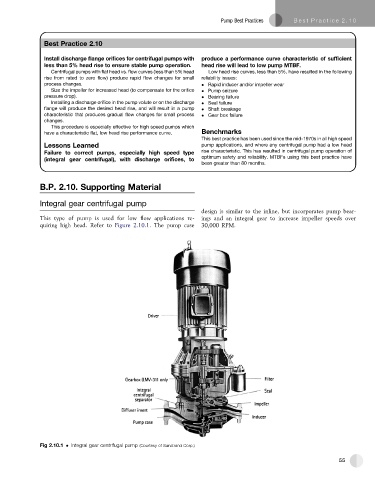
Integral gear centrifugal pump
design is similar to the inline, but incorporates pump bear-
This type of pump is used for low flow applications re- ings and an integral gear to increase impeller speeds over
quiring high head. Refer to Figure 2.10.1. The pump case 30,000 RPM.
Fig 2.10.1 Integral gear centrifugal pump (Courtesy of Sunstrand Corp.)
55