Page 37 - T. Anderson-Fracture Mechanics - Fundamentals and Applns.-CRC (2005)
P. 37
1656_C01.fm Page 17 Tuesday, April 12, 2005 5:55 PM
History and Overview 17
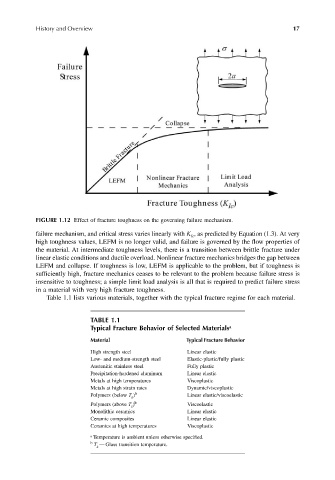
FIGURE 1.12 Effect of fracture toughness on the governing failure mechanism.
failure mechanism, and critical stress varies linearly with K , as predicted by Equation (1.3). At very
Ic
high toughness values, LEFM is no longer valid, and failure is governed by the flow properties of
the material. At intermediate toughness levels, there is a transition between brittle fracture under
linear elastic conditions and ductile overload. Nonlinear fracture mechanics bridges the gap between
LEFM and collapse. If toughness is low, LEFM is applicable to the problem, but if toughness is
sufficiently high, fracture mechanics ceases to be relevant to the problem because failure stress is
insensitive to toughness; a simple limit load analysis is all that is required to predict failure stress
in a material with very high fracture toughness.
Table 1.1 lists various materials, together with the typical fracture regime for each material.
TABLE 1.1
Typical Fracture Behavior of Selected Materials a
Material Typical Fracture Behavior
High strength steel Linear elastic
Low- and medium-strength steel Elastic-plastic/fully plastic
Austenitic stainless steel Fully plastic
Precipitation-hardened aluminum Linear elastic
Metals at high temperatures Viscoplastic
Metals at high strain rates Dynamic/viscoplastic
Polymers (below T g ) b Linear elastic/viscoelastic
Polymers (above T g ) b Viscoelastic
Monolithic ceramics Linear elastic
Ceramic composites Linear elastic
Ceramics at high temperatures Viscoplastic
a Temperature is ambient unless otherwise specified.
b
T g — Glass transition temperature.