Page 60 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 60
46 From smart grid to internet of energy
measurements and the requirements for synchronization and data rates in the
transmission of measurements. IEEE C37.2 standard defines electrical power
system device function numbers, acronyms, and contact designations. The func-
tions of each device used in electrical equipments are defined with a device
function number including a prefix and a suffix for identification. The desig-
nated numbers are used to imply devices in schematics, connection diagrams,
specifications and manuals [36–38].
1.3.2 Phasor measurement units
The PMU which is also defined as synchrophasor is fundamental component of
a Wide Area Monitoring Protection and Control (WAMPAC) system. A PMU
acquires current and voltage waveforms of the power system by using trans-
formers and generates their phasor by sampling measured data. The generated
phasor of current and voltage are complex representation of magnitude and
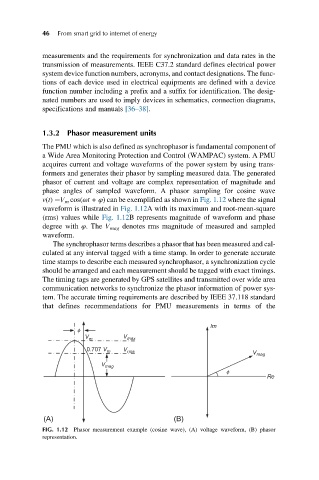
phase angles of sampled waveform. A phasor sampling for cosine wave
v(t) ¼V m cos(ωt+ φ) can be exemplified as shown in Fig. 1.12 where the signal
waveform is illustrated in Fig. 1.12A with its maximum and root-mean-square
(rms) values while Fig. 1.12B represents magnitude of waveform and phase
degree with φ. The V mag denotes rms magnitude of measured and sampled
waveform.
The synchrophasor terms describes a phasor that has been measured and cal-
culated at any interval tagged with a time stamp. In order to generate accurate
time stamps to describe each measured synchrophasor, a synchronization cycle
should be arranged and each measurement should be tagged with exact timings.
The timing tags are generated by GPS satellites and transmitted over wide area
communication networks to synchronize the phasor information of power sys-
tem. The accurate timing requirements are described by IEEE 37.118 standard
that defines recommendations for PMU measurements in terms of the
f V m V max lm
0.707 V m
V rms
V mag
f V mag
Re
(A) (B)
FIG. 1.12 Phasor measurement example (cosine wave), (A) voltage waveform, (B) phasor
representation.