Page 81 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 81
Smart metering and smart monitoring systems Chapter 2 67
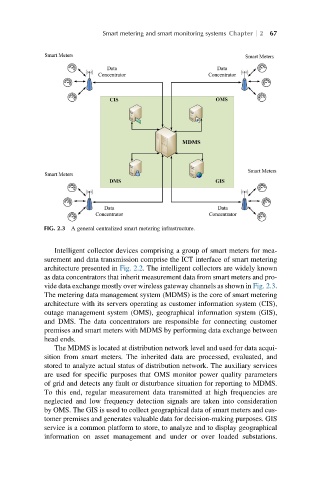
FIG. 2.3 A general centralized smart metering infrastructure.
Intelligent collector devices comprising a group of smart meters for mea-
surement and data transmission comprise the ICT interface of smart metering
architecture presented in Fig. 2.2. The intelligent collectors are widely known
as data concentrators that inherit measurement data from smart meters and pro-
vide data exchange mostly over wireless gateway channels as shown in Fig. 2.3.
The metering data management system (MDMS) is the core of smart metering
architecture with its servers operating as customer information system (CIS),
outage management system (OMS), geographical information system (GIS),
and DMS. The data concentrators are responsible for connecting customer
premises and smart meters with MDMS by performing data exchange between
head ends.
The MDMS is located at distribution network level and used for data acqui-
sition from smart meters. The inherited data are processed, evaluated, and
stored to analyze actual status of distribution network. The auxiliary services
are used for specific purposes that OMS monitor power quality parameters
of grid and detects any fault or disturbance situation for reporting to MDMS.
To this end, regular measurement data transmitted at high frequencies are
neglected and low frequency detection signals are taken into consideration
by OMS. The GIS is used to collect geographical data of smart meters and cus-
tomer premises and generates valuable data for decision-making purposes. GIS
service is a common platform to store, to analyze and to display geographical
information on asset management and under or over loaded substations.