Page 131 - Fundamentals of Communications Systems
P. 131
Complex Baseband Representation of Bandpass Signals 4.7
1
0.8
1
0.6
0.5 0.4
0.2
x Q (t) 0 x Q (t) 0
−0.5 −0.2
−0.4
−1 −0.6
0 1
0.5 0.5
1 −0.8
1.5 0
2 −0.5 −1
I
Time, t/f m 2.5 3 −1 x (t) −1 −0.8 −0.6 −0.4 −0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
x (t)
I
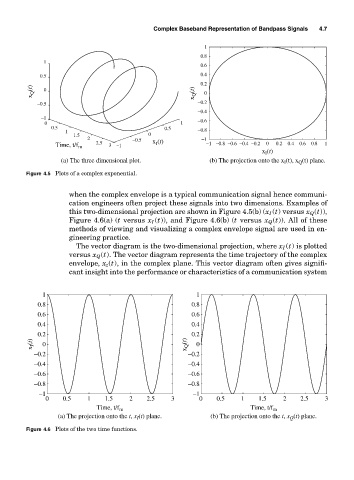
(a) The three dimensional plot. (b) The projection onto the x (t), x (t) plane.
I
Q
Figure 4.5 Plots of a complex exponential.
when the complex envelope is a typical communication signal hence communi-
cation engineers often project these signals into two dimensions. Examples of
this two-dimensional projection are shown in Figure 4.5(b) (x I (t) versus x Q (t)),
Figure 4.6(a) (t versus x I (t)), and Figure 4.6(b) (t versus x Q (t)). All of these
methods of viewing and visualizing a complex envelope signal are used in en-
gineering practice.
The vector diagram is the two-dimensional projection, where x I (t) is plotted
versus x Q (t). The vector diagram represents the time trajectory of the complex
envelope, x z (t), in the complex plane. This vector diagram often gives signifi-
cant insight into the performance or characteristics of a communication system
1 1
0.8 0.8
0.6 0.6
0.4 0.4
0.2 0.2
x I (t) 0 x Q (t) 0
−0.2 −0.2
−0.4 −0.4
−0.6 −0.6
−0.8 −0.8
−1 −1
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
Time, t/f m Time, t/f m
(a) The projection onto the t, x (t) plane. (b) The projection onto the t, x (t) plane.
Q
I
Figure 4.6 Plots of the two time functions.