Page 235 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 235
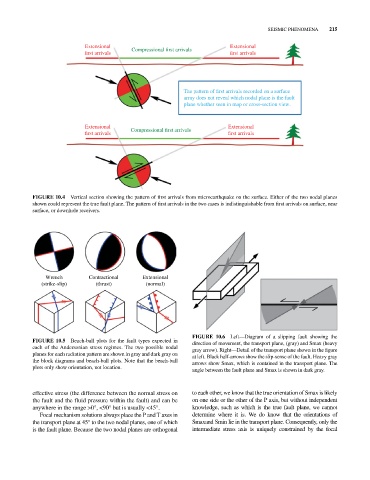
SEISMIC PHENOMENA 215
Extensional Extensional
rst arrivals Compressional rst arrivals rst arrivals
The pattern of rst arrivals recorded on a surface
array does not reveal which nodal plane is the fault
plane whether seen in map or cross-section view.
Extensional Compressional rst arrivals Extensional
rst arrivals rst arrivals
FIGURE 10.4 Vertical section showing the pattern of first arrivals from microearthquake on the surface. Either of the two nodal planes
shown could represent the true fault plane. The pattern of first arrivals in the two cases is indistinguishable from first arrivals on surface, near
surface, or downhole receivers.
Wrench Contractional Extensional
(strike-slip) (thrust) (normal)
FIGURE 10.6 Left—Diagram of a slipping fault showing the
FIGURE 10.5 Beach‐ball plots for the fault types expected in direction of movement, the transport plane, (gray) and Smax (heavy
each of the Andersonian stress regimes. The two possible nodal gray arrow). Right—Detail of the transport plane shown in the figure
planes for each radiation pattern are shown in gray and dark gray on at left. Black half‐arrows show the slip‐sense of the fault. Heavy gray
the block diagrams and beach‐ball plots. Note that the beach‐ball arrows show Smax, which is contained in the transport plane. The
plots only show orientation, not location. angle between the fault plane and Smax is shown in dark gray.
effective stress (the difference between the normal stress on to each other, we know that the true orientation of Smax is likely
the fault and the fluid pressure within the fault) and can be on one side or the other of the P axis, but without independent
anywhere in the range >0°, <90° but is usually <45°. knowledge, such as which is the true fault plane, we cannot
Focal mechanism solutions always place the P and T axes in determine where it is. We do know that the orientations of
the transport plane at 45° to the two nodal planes, one of which Smaxand Smin lie in the transport plane. Consequently, only the
is the fault plane. Because the two nodal planes are orthogonal intermediate stress axis is uniquely constrained by the focal