Page 150 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 150
Functions of Random Variables 133
Hence, using Equation (5.25),
2
1
X dg
y
j
1
f
y f g
y
Y
X
j
j1 dy
f
y 1=2 f
y 1=2
X X
2y 1=2 2y 1=2
1
y=2
e ;
2 y 1=2
or
1
y=2
8
< e ; for y 0;
f
y
2 y 1=2
5:28
Y
:
0; elsewhere:
This is the so-called 2 distribution, to be discussed in more detail in Section
7.4.2.
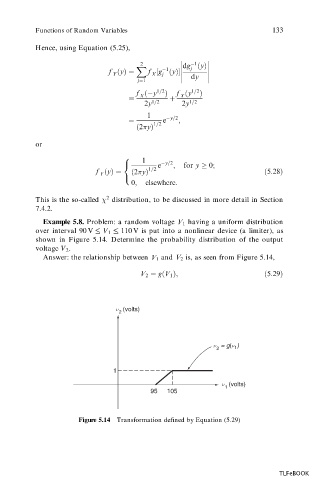
Example 5.8. Problem: a random voltage V 1 having a uniform distribution
over interval 90 V V 1 110 V is put into a nonlinear device (a limiter), as
shown in Figure 5.14. Determine the probability distribution of the output
voltage V 2 .
Answer: the relationship between V 1 and V 2 is, as seen from Figure 5.14,
V 2 g
V 1 ;
5:29
ν (volts)
2
ν = g( )
ν
2 1
1
ν (volts)
1
95 105
Figure 5.14 Transformation defined by Equation (5.29)
TLFeBOOK