Page 194 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 194
Some Important Discrete Distributions 177
p (0,t)
k
0.6
p (0,t)
k
0.4 0.4
0.2 0.2
0 k 0 k
0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
(a) (b)
p (0,t)
k
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
k
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
(c)
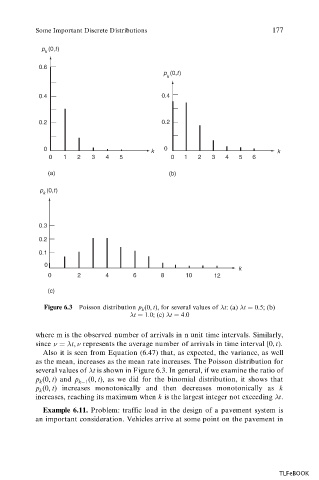
Figure 6.3 Poisson distribution p (0, t), for several values of t: (a) t 0:5; (b)
k
t 1:0; (c) t 4:0
where m is the observed number of arrivals in n unit time intervals. Similarly,
since t, represents the average number of arrivals in time interval [0, t).
Also it is seen from Equation (6.47) that, as expected, the variance, as well
as the mean, increases as the mean rate increases. The Poisson distribution for
several values of t is shown in Figure 6.3. In general, if we examine the ratio of
p (0, t) and p (0, t), as we did for the binomial distribution, it shows that
k k 1
p (0, t) increases monotonically and then decreases monotonically as k
k
increases, reaching its maximum when k is the largest integer not exceeding t.
Example 6.11. Problem: traffic load in the design of a pavement system is
an important consideration. Vehicles arrive at some point on the pavement in
TLFeBOOK