Page 77 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 77
60 Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
Similarly,
1
8
; for 0 y 60;
<
f
y 60
Y
:
0; elsewhere:
Both random variables are thus uniformly distributed over the interval (0, 60).
Example 3.8. In structural reliability studies, the resistance Y of a structural
element and the force X applied to it are generally regarded as random vari-
ables. The probability of failure, p f , is defined by P(Y X ). Suppose that the
jpdf of X and Y is specified to be
axby
abe ; for
x; y > 0;
f
x; y
XY
0; for
x; y 0;
where a and b are known positive constants, we wish to determine p f .
The probability p f is determined from
Z Z
p f f XY
x; ydxdy;
R
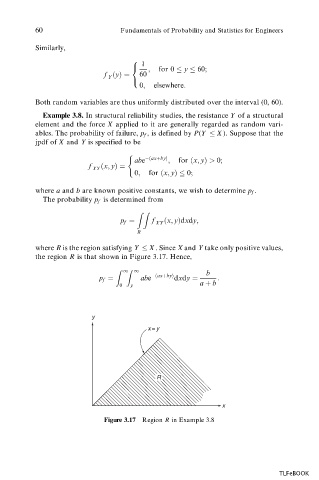
where R is the region satisfying Y X . Since X and Y take only positive values,
the region R is that shown in Figure 3.17. Hence,
1
Z Z 1 b
p f abe
axby dxdy :
0 y a b
y
x = y
R
x
Figure 3.17 Region R in Example 3.8
TLFeBOOK