Page 287 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 287
OILWELL TESTING 224
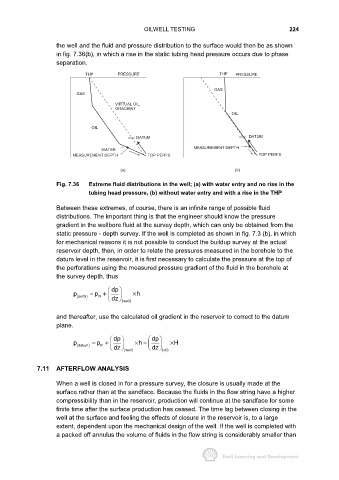
the well and the fluid and pressure distribution to the surface would then be as shown
in fig. 7.36(b), in which a rise in the static tubing head pressure occurs due to phase
separation.
THP PRESSURE THP PRESSURE
GAS
GAS
VIRTUAL OIL
GRADIENT
OIL
OIL
DATUM DATUM
WATER MEASUREMENT DEPTH
MEASUREMENT DEPTH TOP PERFS. TOP PERFS.
(a) (b)
Fig. 7.36 Extreme fluid distributions in the well; (a) with water entry and no rise in the
tubing head pressure, (b) without water entry and with a rise in the THP
Between these extremes, of course, there is an infinite range of possible fluid
distributions. The important thing is that the engineer should know the pressure
gradient in the wellbore fluid at the survey depth, which can only be obtained from the
static pressure - depth survey. If the well is completed as shown in fig. 7.3 (b), in which
for mechanical reasons it is not possible to conduct the buildup survey at the actual
reservoir depth, then, in order to relate the pressures measured in the borehole to the
datum level in the reservoir, it is first necessary to calculate the pressure at the top of
the perforations using the measured pressure gradient of the fluid in the borehole at
the survey depth, thus
dp
p (perfs ) = p + × h
m
dz (well )
and thereafter, use the calculated oil gradient in the reservoir to correct to the datum
plane.
dp dp
p (datum ) = p + × h − × H
m
dz (well ) dz ( )
oil
7.11 AFTERFLOW ANALYSIS
When a well is closed in for a pressure survey, the closure is usually made at the
surface rather than at the sandface. Because the fluids in the flow string have a higher
compressibility than in the reservoir, production will continue at the sandface for some
finite time after the surface production has ceased. The time lag between closing in the
well at the surface and feeling the effects of closure in the reservoir is, to a large
extent, dependent upon the mechanical design of the well. If the well is completed with
a packed off annulus the volume of fluids in the flow string is considerably smaller than