Page 143 - Fundamentals of The Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow
P. 143
STEADY STATE HEAT CONDUCTION IN MULTI-DIMENSIONS
2
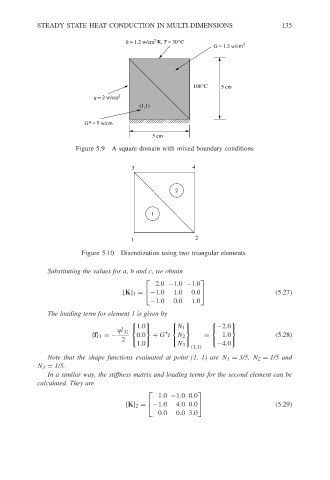
h = 1.2 w/cm K, T = 30°C
100°C G = 1.2 w/cm 3 135
5 cm
q = 2 w/cm 2
(1,1)
G* = 5 w/cm
5 cm
Figure 5.9 A square domain with mixed boundary conditions
3 4
2
1
2
1
Figure 5.10 Discretization using two triangular elements
Substituting the values for a, b and c, we obtain
2.0 −1.0 −1.0
[K] 1 = −1.0 1.0 0.0 (5.27)
−1.0 0.0 1.0
The loading term for element 1 is given by
ql 31 1.0 N 1 −2.0
∗
{f} 1 =− 0.0 + G t N 2 = 1.0 (5.28)
1.0 N 3 −4.0
2
(1,1)
Note that the shape functions evaluated at point (1, 1) are N 1 = 3/5, N 2 = 1/5 and
N 3 = 1/5.
In a similar way, the stiffness matrix and loading terms for the second element can be
calculated. They are
1.0 −1.00.0
[K] 2 = −1.0 4.00.0 (5.29)
0.0 0.03.0