Page 56 - Gas Adsorption Equilibria
P. 56
42 Chapter 1
fades away after a while when the helium is spread out in the system, but
this may take 1-2 hours, i. e. exceed observation times of this experiments
which were about 15 minutes [1.48].
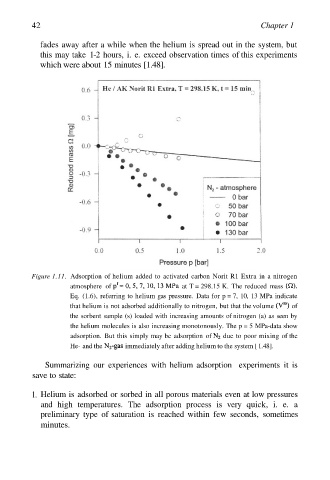
Figure 1.11. Adsorption of helium added to activated carbon Norit R1 Extra in a nitrogen
atmosphere of at T = 298.15 K. The reduced mass
Eq. (1.6), referring to helium gas pressure. Data for p = 7, 10, 13 MPa indicate
that helium is not adsorbed additionally to nitrogen, but that the volume of
the sorbent sample (s) loaded with increasing amounts of nitrogen (a) as seen by
the helium molecules is also increasing monotonously. The p = 5 MPa-data show
adsorption. But this simply may be adsorption of due to poor mixing of the
He- and the immediately after adding helium to the system [ 1.48].
Summarizing our experiences with helium adsorption experiments it is
save to state:
1. Helium is adsorbed or sorbed in all porous materials even at low pressures
and high temperatures. The adsorption process is very quick, i. e. a
preliminary type of saturation is reached within few seconds, sometimes
minutes.