Page 159 - Geochemical Anomaly and Mineral Prospectivity Mapping in GIS
P. 159
160 Chapter 6
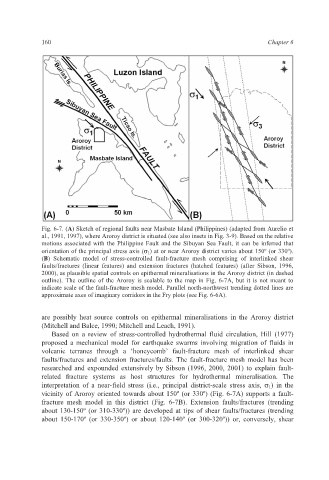
Fig. 6-7. (A) Sketch of regional faults near Masbate Island (Philippines) (adapted from Aurelio et
al., 1991, 1997), where Aroroy district is situated (see also insets in Fig. 3-9). Based on the relative
motions associated with the Philippine Fault and the Sibuyan Sea Fault, it can be inferred that
orientation of the principal stress axis (σ 1 ) at or near Aroroy district varies about 150º (or 330º).
(B) Schematic model of stress-controlled fault-fracture mesh comprising of interlinked shear
faults/fractures (linear features) and extension fractures (hatched features) (after Sibson, 1996,
2000), as plausible spatial controls on epithermal mineralisations in the Aroroy district (in dashed
outline). The outline of the Aroroy is scalable to the map in Fig. 6-7A, but it is not meant to
indicate scale of the fault-fracture mesh model. Parallel north-northwest trending dotted lines are
approximate axes of imaginary corridors in the Fry plots (see Fig. 6-6A).
are possibly heat source controls on epithermal mineralisations in the Aroroy district
(Mitchell and Balce, 1990; Mitchell and Leach, 1991).
Based on a review of stress-controlled hydrothermal fluid circulation, Hill (1977)
proposed a mechanical model for earthquake swarms involving migration of fluids in
volcanic terranes through a ‘honeycomb’ fault-fracture mesh of interlinked shear
faults/fractures and extension fractures/faults. The fault-fracture mesh model has been
researched and expounded extensively by Sibson (1996, 2000, 2001) to explain fault-
related fracture systems as host structures for hydrothermal mineralisation. The
interpretation of a near-field stress (i.e., principal district-scale stress axis, σ 1) in the
vicinity of Aroroy oriented towards about 150º (or 330º) (Fig. 6-7A) supports a fault-
fracture mesh model in this district (Fig. 6-7B). Extension faults/fractures (trending
about 130-150º (or 310-330º)) are developed at tips of shear faults/fractures (trending
about 150-170º (or 330-350º) or about 120-140º (or 300-320º)) or, conversely, shear