Page 38 - Geochemical Anomaly and Mineral Prospectivity Mapping in GIS
P. 38
34 Chapter 2
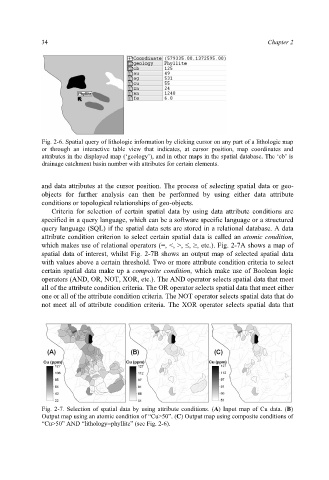
Fig. 2-6. Spatial query of lithologic information by clicking cursor on any part of a lithologic map
or through an interactive table view that indicates, at cursor position, map coordinates and
attributes in the displayed map (‘geology’), and in other maps in the spatial database. The ‘cb’ is
drainage catchment basin number with attributes for certain elements.
and data attributes at the cursor position. The process of selecting spatial data or geo-
objects for further analysis can then be performed by using either data attribute
conditions or topological relationships of geo-objects.
Criteria for selection of certain spatial data by using data attribute conditions are
specified in a query language, which can be a software specific language or a structured
query language (SQL) if the spatial data sets are stored in a relational database. A data
attribute condition criterion to select certain spatial data is called an atomic condition,
which makes use of relational operators (=, <, >, , , etc.). Fig. 2-7A shows a map of
spatial data of interest, whilst Fig. 2-7B shows an output map of selected spatial data
with values above a certain threshold. Two or more attribute condition criteria to select
certain spatial data make up a composite condition, which make use of Boolean logic
operators (AND, OR, NOT, XOR, etc.). The AND operator selects spatial data that meet
all of the attribute condition criteria. The OR operator selects spatial data that meet either
one or all of the attribute condition criteria. The NOT operator selects spatial data that do
not meet all of attribute condition criteria. The XOR operator selects spatial data that
Fig. 2-7. Selection of spatial data by using attribute conditions. (A) Input map of Cu data. (B)
Output map using an atomic condition of “Cu>50”. (C) Output map using composite conditions of
“Cu>50” AND “lithology=phyllite” (see Fig. 2-6).