Page 357 - Handbook Of Integral Equations
P. 357
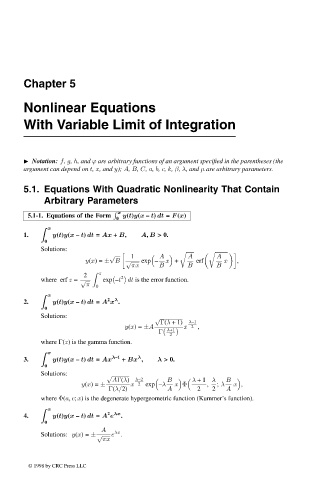
Chapter 5
Nonlinear Equations
With Variable Limit of Integration
Notation: f, g, h, and ϕ are arbitrary functions of an argument specified in the parentheses (the
argument can depend on t, x, and y); A, B, C, a, b, c, k, β, λ, and µ are arbitrary parameters.
5.1. Equations With Quadratic Nonlinearity That Contain
Arbitrary Parameters
x
5.1-1. Equations of the Form y(t)y(x – t) dt = F (x)
0
x
1. y(t)y(x – t) dt = Ax + B, A, B >0.
0
Solutions:
√ 1 A A A
y(x)= ± B √ exp – x + erf x ,
πx B B B
z
2 2
where erf z = √ exp –t dt is the error function.
π 0
x
2
λ
2. y(t)y(x – t) dt = A x .
0
Solutions: √
Γ(λ +1) λ–1
y(x)= ±A x 2 ,
Γ λ+1
2
where Γ(z) is the gamma function.
x
λ
3. y(t)y(x – t) dt = Ax λ–1 + Bx , λ >0.
0
Solutions: √
AΓ(λ) λ–2 B λ +1 λ B
y(x)= ± x 2 exp –λ x Φ , ; λ x ,
Γ(λ/2) A 2 2 A
where Φ(a, c; x) is the degenerate hypergeometric function (Kummer’s function).
x
2 λx
4. y(t)y(x – t) dt = A e .
0
A λx
Solutions: y(x)= ± √ e .
πx
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
Page 337