Page 700 - Handbook Of Integral Equations
P. 700
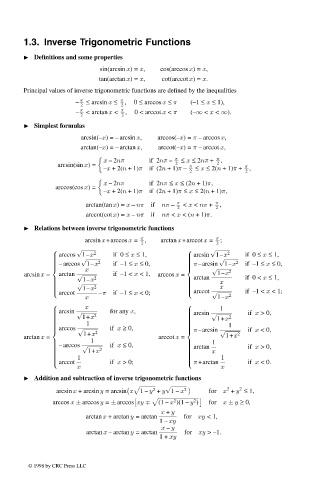
1.3. Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Definitions and some properties
sin(arcsin x)= x, cos(arccos x)= x,
tan(arctan x)= x, cot(arccot x)= x.
Principal values of inverse trigonometric functions are defined by the inequalities
– π ≤ arcsin x ≤ π , 0 ≤ arccos x ≤ π (–1 ≤ x ≤ 1),
2 2
– π < arctan x < π , 0 < arccot x < π (–∞ < x < ∞).
2 2
Simplest formulas
arcsin(–x)= – arcsin x, arccos(–x)= π – arccos x,
arctan(–x)= – arctan x, arccot(–x)= π – arccot x,
x – 2nπ if 2nπ – ≤ x ≤ 2nπ + ,
π π
arcsin(sin x)= 2 π 2 π
–x +2(n +1)π if (2n +1)π – ≤ x ≤ 2(n +1)π + ,
2 2
x – 2nπ if 2nπ ≤ x ≤ (2n +1)π,
arccos(cos x)=
–x +2(n +1)π if (2n +1)π ≤ x ≤ 2(n +1)π,
arctan(tan x)= x – nπ if nπ – π < x < nπ + π ,
2 2
arccot(cot x)= x – nπ if nπ < x <(n +1)π.
Relations between inverse trigonometric functions
arcsin x+arccos x = π , arctan x+arccot x = π ;
2 2
√ √
2 2
arccos 1–x if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, arcsin 1–x if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1,
√ √
2 2
– arccos 1–x if –1 ≤ x ≤ 0, π–arcsin 1–x if –1 ≤ x ≤ 0,
x 2
√
arcsin x = arctan √ if –1< x <1, arccos x = 1–x
1–x 2 arctan if 0 < x ≤ 1,
√ x
1–x
2 x
arccot √ if –1< x <1;
arccot –π if –1 ≤ x <0;
x 1–x 2
x 1
arcsin √ for any x, if x >0,
arcsin √
1+x 2
2
1+x
1
1
arccos √ if x ≥ 0, if x <0,
1+x 2 π–arcsin √ 2
arctan x = arccot x = 1+x
1
1
– arccos √ if x ≤ 0, arctan if x >0,
1+x
2
x
1 1
arccot if x >0; π+arctan if x <0.
x x
Addition and subtraction of inverse trigonometric functions
√
2 2
2
arcsin x + arcsin y = arcsin x 1 – y + y 1 – x 2 for x + y ≤ 1,
2
2
arccos x ± arccos y = ± arccos xy ∓ (1 – x )(1 – y ) for x ± y ≥ 0,
x + y
arctan x + arctan y = arctan for xy <1,
1 – xy
x – y
arctan x – arctan y = arctan for xy > –1.
1+ xy
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
© 1998 by CRC Press LLC
Page 684