Page 452 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 452
424 14 Lithium Alloy Anodes
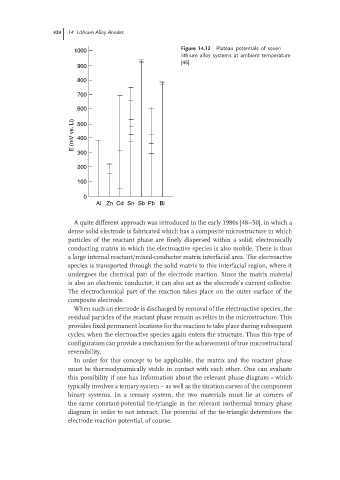
Figure 14.12 Plateau potentials of seven
1000
lithium alloy systems at ambient temperature
[46].
900
800
700
600
E (mV vs. Li) 500
400
300
200
100
0
Al Zn Cd Sn Sb Pb Bi
A quite different approach was introduced in the early 1980s [48–50], in which a
dense solid electrode is fabricated which has a composite microstructure in which
particles of the reactant phase are finely dispersed within a solid, electronically
conducting matrix in which the electroactive species is also mobile. There is thus
a large internal reactant/mixed-conductor matrix interfacial area. The electroactive
species is transported through the solid matrix to this interfacial region, where it
undergoes the chemical part of the electrode reaction. Since the matrix material
is also an electronic conductor, it can also act as the electrode’s current collector.
The electrochemical part of the reaction takes place on the outer surface of the
composite electrode.
When such an electrode is discharged by removal of the electroactive species, the
residual particles of the reactant phase remain as relics in the microstructure. This
provides fixed permanent locations for the reaction to take place during subsequent
cycles, when the electroactive species again enters the structure. Thus this type of
configuration can provide a mechanism for the achievement of true microstructural
reversibility.
In order for this concept to be applicable, the matrix and the reactant phase
must be thermodynamically stable in contact with each other. One can evaluate
this possibility if one has information about the relevant phase diagram – which
typically involves a ternary system – as well as the titration curves of the component
binary systems. In a ternary system, the two materials must lie at corners of
the same constant-potential tie-triangle in the relevant isothermal ternary phase
diagram in order to not interact. The potential of the tie-triangle determines the
electrode reaction potential, of course.