Page 98 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 98
64 2 Practical Batteries
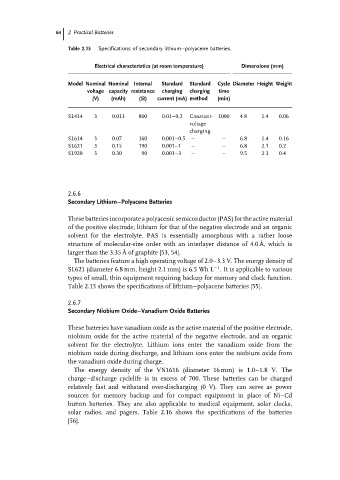
Table 2.15 Specifications of secondary lithium–polyacene batteries.
Electrical characteristics (at room temperature) Dimensions (mm)
Model Nominal Nominal Internal Standard Standard Cycle Diameter Height Weight
voltage capacity resistance charging charging time
(V) (mAh) (Ω) current (mA) method (min)
SL414 3 0.013 800 0.01–0.2 Constant- 1000 4.8 1.4 0.06
voltage
charging
SL614 3 0.07 160 0.001–0.5 – – 6.8 1.4 0.16
SL621 3 0.15 190 0.001–1 – – 6.8 2.1 0.2
SL920 3 0.30 90 0.001–3 – – 9.5 2.1 0.4
2.6.6
Secondary Lithium–Polyacene Batteries
These batteries incorporate a polyacenic semiconductor (PAS) for the active material
of the positive electrode, lithium for that of the negative electrode and an organic
solvent for the electrolyte. PAS is essentially amorphous with a rather loose
structure of molecular-size order with an interlayer distance of 4.0 ˚ A, which is
larger than the 3.35 ˚ A of graphite [53, 54].
The batteries feature a high operating voltage of 2.0–3.3 V. The energy density of
−1
SL621 (diameter 6.8 mm, height 2.1 mm) is 6.5 Wh L . It is applicable to various
types of small, thin equipment requiring backup for memory and clock function.
Table 2.15 shows the specifications of lithium–polyacene batteries [55].
2.6.7
Secondary Niobium Oxide–Vanadium Oxide Batteries
These batteries have vanadium oxide as the active material of the positive electrode,
niobium oxide for the active material of the negative electrode, and an organic
solvent for the electrolyte. Lithium ions enter the vanadium oxide from the
niobium oxide during discharge, and lithium ions enter the niobium oxide from
the vanadium oxide during charge.
The energy density of the VN1616 (diameter 16 mm) is 1.0–1.8 V. The
charge–discharge cyclelife is in excess of 700. These batteries can be charged
relatively fast and withstand over-discharging (0 V). They can serve as power
sources for memory backup and for compact equipment in place of Ni–Cd
button batteries. They are also applicable to medical equipment, solar clocks,
solar radios, and pagers. Table 2.16 shows the specifications of the batteries
[56].