Page 100 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 100
66 2 Practical Batteries
2.7
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are generally composed of lithium containing a
transition-metal oxide as the positive electrode material and a carbon material
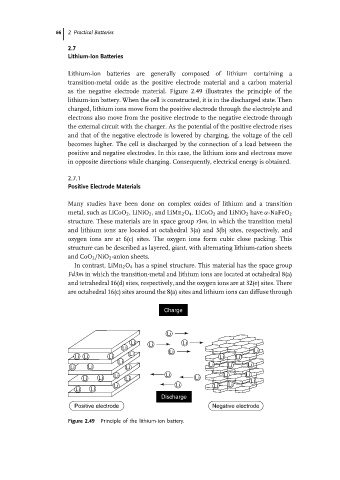
as the negative electrode material. Figure 2.49 illustrates the principle of the
lithium-ion battery. When the cell is constructed, it is in the discharged state. Then
charged, lithium ions move from the positive electrode through the electrolyte and
electrons also move from the positive electrode to the negative electrode through
the external circuit with the charger. As the potential of the positive electrode rises
and that of the negative electrode is lowered by charging, the voltage of the cell
becomes higher. The cell is discharged by the connection of a load between the
positive and negative electrodes. In this case, the lithium ions and electrons move
in opposite directions while charging. Consequently, electrical energy is obtained.
2.7.1
Positive Electrode Materials
Many studies have been done on complex oxides of lithium and a transition
metal, such as LiCoO 2 , LiNiO 2 , and LiMn 2 O 4 .LiCoO 2 and LiNiO 2 have α-NaFeO 2
structure. These materials are in space group r3m, in which the transition metal
and lithium ions are located at octahedral 3(a) and 3(b) sites, respectively, and
oxygen ions are at 6(c) sites. The oxygen ions form cubic close packing. This
structure can be described as layered, giant, with alternating lithium-cation sheets
and CoO 2 /NiO 2 -anion sheets.
In contrast, LiMn 2 O 4 has a spinel structure. This material has the space group
Fd3m in which the transition-metal and lithium ions are located at octahedral 8(a)
and tetrahedral 16(d) sites, respectively, and the oxygen ions are at 32(e) sites. There
are octahedral 16(c) sites around the 8(a) sites and lithium ions can diffuse through
Charge
Li
Li Li Li
Li Li
Li Li
Li Li Li Li Li
Li
Li Li Li Li Li Li
Li Li Li Li
Li Li Li Li Li
Li Li Li Li
Li Li
Discharge
Positive electrode Negative electrode
Figure 2.49 Principle of the lithium-ion battery.