Page 282 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 282
PRESTRESSED CONCRETE 2.67
1.5
Thus, using the ACI Code, E c (145) (33)(4000) 0.5 3,644,000 lb/sq.in. (25,125.4
MPa).
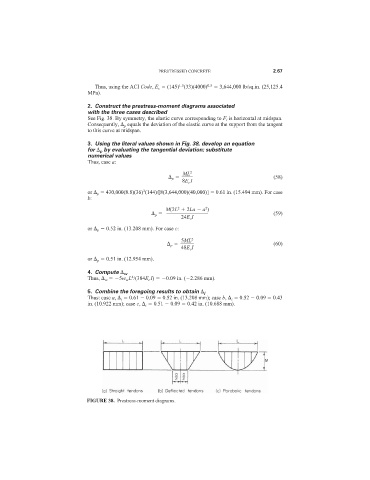
2. Construct the prestress-moment diagrams associated
with the three cases described
See Fig. 38. By symmetry, the elastic curve corresponding to F i is horizontal at midspan.
Consequently, p equals the deviation of the elastic curve at the support from the tangent
to this curve at midspan.
3. Using the literal values shown in Fig. 38, develop an equation
for p by evaluating the tangential deviation; substitute
numerical values
Thus, case a:
ML 2
p (58)
8E c I
2
or p 430,000(8.8)(36) (144)/[8(3,644,000)(40,000)] 0.61 in. (15.494 mm). For case
b:
2
2
M(2L 2La a )
p (59)
24E c I
or p 0.52 in. (13.208 mm). For case c:
5ML 2
p (60)
48E c I
or p 0.51 in. (12.954 mm).
4. Compute w
4
Thus, w 5w w L /(384E c I) 0.09 in. ( 2.286 mm).
5. Combine the foregoing results to obtain j
Thus: case a, i 0.61 0.09 0.52 in. (13.208 mm); case b, i 0.52 0.09 0.43
in. (10.922 mm); case c, i 0.51 0.09 0.42 in. (10.688 mm).
FIGURE 38. Prestress-moment diagrams.