Page 266 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 266
Chapter 9 Applications of deep learning in biomedical engineering 257
21. Image segmentation
Segmentation is the process of extracting region of interest in
the human anatomical images. The basic aim of this segregation
is to make the images easy to analyze and interpret by preserving
the quality. This technique labels the pixels according to their in-
tensity and characteristics and exploits them accordingly to
perform segmentation. DL techniques outperformed the tradi-
tional methods by directly learning the feature information
from the input images [18].
Segmentation is used for fatal disease analysis, quantifying
tissue sizes, analyzing anatomical structures and their functions,
3D rendering technique, visualization using virtual reality, and
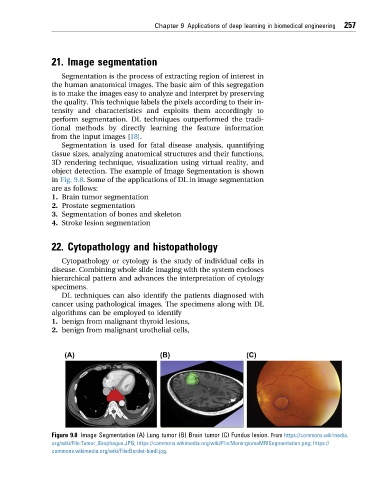
object detection. The example of Image Segmentation is shown
in Fig. 9.8. Some of the applications of DL in image segmentation
are as follows:
1. Brain tumor segmentation
2. Prostate segmentation
3. Segmentation of bones and skeleton
4. Stroke lesion segmentation
22. Cytopathology and histopathology
Cytopathology or cytology is the study of individual cells in
disease. Combining whole slide imaging with the system encloses
hierarchical pattern and advances the interpretation of cytology
specimens.
DL techniques can also identify the patients diagnosed with
cancer using pathological images. The specimens along with DL
algorithms can be employed to identify
1. benign from malignant thyroid lesions,
2. benign from malignant urothelial cells,
Figure 9.8 Image Segmentation (A) Lung tumor (B) Brain tumor (C) Fundus lesion. From https://commons.wikimedia.
org/wiki/File:Tumor_Esophagus.JPG; https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:MeningiomaMRISegmentation.png; https://
commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bardet-biedl.jpg.